The growth when it comes to single-use technologies has gone on to redefine modern biomanufacturing. Once regarded as a very niche choice, single-use assemblies (SUAs) have gone on to become an integral part of upstream and downstream as well as full-finish operations, specifically when it comes to the production of monoclinic antibodies, cell and gene therapy, along with small batch biologics. The communication is loud and clear: decreased cleaning validation, lower capital costs, rapid changeovers, and, of course, minimized cross-contamination risks.
However, with these kinds of advantages, there comes a critical responsibility, which is validation. Regulatory bodies, along with the end users, happen to demand high confidence when it comes to dependence, consistency, and safety of disposable components. As single-use systems happen to get designed for one-time use only and are often produced offsite by third-party vendors, validation goes on to become a technical as well as compliance imperative.
Right from making sure that leachables as well as extractables happen to be within the safe limits to sterility assurance and mechanical integrity, the gamut of validation happens to be very evolving and broad.
Understanding the single-use assemblies when it comes to biomanufacturing
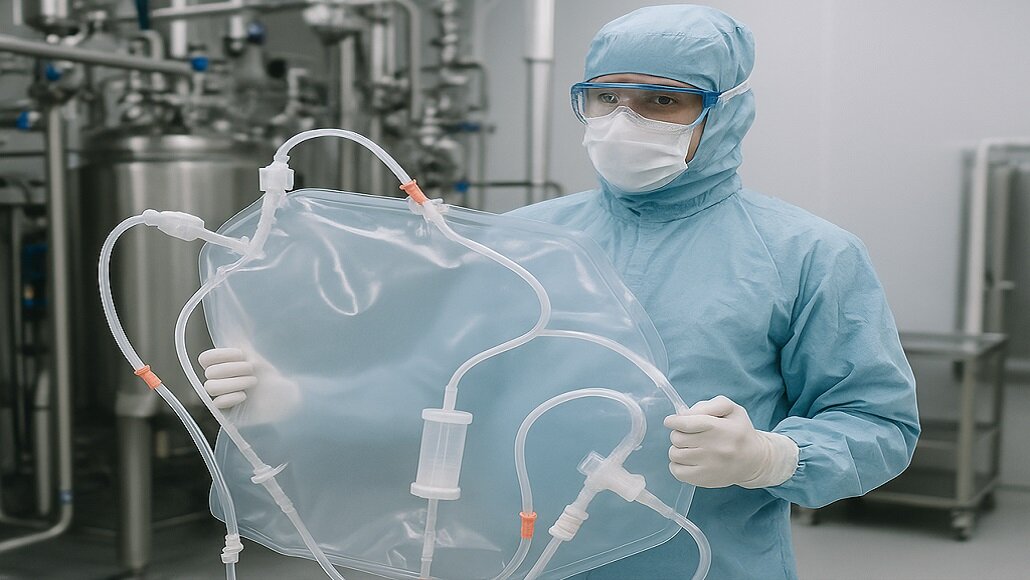
Single-use assembly – SUAs happen to be pre-sterilised systems, and disposable and are, in fact, made up of components such as connectors, tubing, and filters, as well as bags, and are designed to handle fluid transfer in numerous stages when it comes to bioprocessing.
These systems happen to be typically delivered in the form of custom-configured and ready-to-use units that eradicate the requirement when it comes to traditional cleaning as well as sterilization procedures like CIP – clean in place as well as SIP – steam in place.
The adoption when it comes to SUAs has rapidly grown because of their capacity to decrease the turnaround time, support flexible and multiproduct manufacturing environments, and at the same time decrease the cross-contamination risk. This happens to be commonly used when it comes to upstream as well as downstream operations, right from media preparation to final fill and finish, thereby helping with faster production cycles.
But the disposition of SU goes on to introduce some unique barriers and challenges. As each of the assemblies happens to be used only once, the manufacturers must please place much greater stress on initial validation, supply chain, liability, and, of course, material compatibility. The materials that are used are typically advanced polymers and have to remain stable when it comes to sterilization as well as with prolonged fluid exposure without any kind of contaminant introduction.
Knowing such a kind of assembly is indeed very crucial, not just because of its operational role, but also because of ensuring process integrity, consistent product quality, and regulatory compliance in an industry that is very highly regulated.
Why does validation happen to matter more when it comes to single-use systems?
Unlike the traditional stainless steel systems, which happened to be validated once and are cleaned repeatedly, single-use assemblies have to be validated at the component, material, and system levels every time they have to be used in critical operations. The validation makes sure that
The materials that are used do not leach any harmful chemicals.
The system goes to maintain mechanical integrity, and that too under pressure as well as process conditions.
The system happens to be compatible along with the process fluids as well as the biologics that are involved.
The sterilization method, which is typically gamma irradiation, happens to be effective and doesn’t degrade the performance of the component.
As most of the single-use systems get assembled as well as sterilized offsite, biomanufacturers must also go ahead and validate the supplier quality systems by adding one more layer in terms of intricacy to the compliance.
What are the key validation barriers?
Leachables as well as extractables
One of the most pressing issues when it comes to single-use validation happens to be the risk of chemical migration. Extractables happen to be compounds that can be extracted right from the materials when they are exposed to solvents under certain aggressive conditions, whereas leachables are the ones that actually migrate when it comes to normal operating conditions.
Leachables and extractables studies are indeed necessary in order to confirm that there is no substance that compromises the identity, potency, or purity of the product. These studies have to be specific when it comes to the product formulation, pH, and process, as well as the contract duration. The manufacturers have to determine if the vendor-supplied extractable data can be made use of or if the product-specific leachable studies are indeed necessary.
Mechanical performance along with integrity
Tensile strength, pressure testing, and visual inspection happen to be vital in order to make sure that the assembly can withstand any kind of expected operating conditions. A failure in a connector, a single belt, or a seam can lead to contamination or a product loss and even batch rejection for that matter. Manufacturers have to validate the pressure decay, burst pressure, and flow rate consistency all across the production lots.
Assurance of sterility
It is well to be noted that gamma irradiation happens to be the most common method when it comes to sterilizing single-use assemblies; however, its effect on material properties should be carefully evaluated. Validation has to confirm that sterilization is indeed effective and at the same time also make sure that the radiation has not gone on to compromise the clarity, strength, or extractable profile when it comes to the materials.
Fluid interaction along with compatibility
Every biologic product may as well interact in a different way with polymer surfaces. Absorption when it comes to proteins or even the breakdown of materials has to be evaluated in order to ensure that crucial quality attributes get to be maintained. Compatibility studies are specifically very significant when it comes to cell and gene therapy, wherein small volumes as well as fragile molecules are common.
Making sure of repeatability throughout the batches
One of the barriers when it comes to single-use assembly is that every batch has to perform as predictably as a stainless-steel system, even if the components are not getting reused.
In order to achieve this, manufacturers often go to work with vendors so as to establish
Traceability mechanisms, which include RFID tagging and barcodes, come into play when it comes to batch-level identification.
Component-level specifications, like tolerances, dimensions, and material properties.
Lot-to-lot consistency audits by way of statistical sampling as well as physical testing.
Design the freeze protocols in order to lock critical parameters as well as avoid any kind of unapproved design alterations.
It is well to be noted that repeatability is indeed very vital not just for the product quality but also for regulatory approvals.
The authorities increasingly expect companies to go ahead and demonstrate that disposable components are going to perform in a very identical way every time they are used, specifically when it comes to commercial-scale production.
Navigating the regulatory anticipations
The worldwide regulatory authorities are still evolving on how they go ahead and approach validation when it comes to single-use technologies. But there are several guiding principles that have gone on to emerge.
ISO as well as ASTM standards
It is well to be noted that ISO 11137 as well as ASTM F 1980 happened to offer a framework for sterilization validation as well as speeding up of aging studies. The standards are widely used across validation packages that are submitted to the regulators.
FDA along with EMA guidelines
Both the FDA and the EMA stress that the burden when it comes to validation rests on the drug manufacturer. Even when the components get outsourced, supplier qualification, documentation, and incoming inspection are very crucial. The FDA anticipates that the drug sponsors justify how they have assessed single-use materials, especially when it comes to leachables and extractables, and how they have validated the assembly configurations when it comes to specific processes.
The GMP Annex and Annex 1 updates
It is well to be noted that the revised EU GMP Annex 1 underscores the significance of closed systems along with single-use technologies when it comes to sterile manufacturing. It also happens to place growing emphasis on preventive contamination control, which syncs with the major benefits of disposal systems.
Documentation along with change control
The fact is that proper documentation is very necessary. The change control procedures must go on to cover every minor change, like switching a connector or changing a sterilization batch. Regulatory authorities have to scrutinize such kinds of changes all throughout the inspections, specifically when they affect the product contact surfaces.
Going to a risk-based validation approach
Because of the intricacy as well as the volume of validation that is required, there are many companies that are shifting towards a risk-based kind of approach in order to leverage efforts as well as focus on the highest-impact possibilities.
This kind of approach happens to involve-
Conducting risk evaluation by way of using tools such as failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA)
Giving priority to validation of components when it comes to critical process functionality or direct contact.
Making use of platform studies whenever it is possible so as to avoid any kind of redundant validation throughout the similar systems or products.
Depending on supplier-offered data when justified and supplementing it by certain internal confirmatory testing.
It is well to be noted that risk-based validation not only helps to streamline compliance but at the same time also happens to support much faster tech transfer as well as scale activities to very critical needs when it comes to today’s fast-paced development spectrum.
Conclusion
Single-use assemblies aren’t optional anymore; they are now indispensable when it comes to the design as well as the execution of modern bioprocesses. But their disposable nature goes on to introduce many new layers of responsibility when it comes to traceability, validation, and risk management.
Right from leachables as well as mechanical integrity to sterilization as well as regulatory documentation, validation of single-use assemblies needs to have a multidimensional and proactive approach. Manufacturers have to look beyond the component-level testing and also take into account a system-level view by way of partnering closely with certain suppliers and also enforcing some quality controls that are very tight and are aligning with the ever-evolving regulatory guidance.
As the biologics go on to become more complex and the manufacturing timelines get more compressed, the role when it comes to validated, dependable single-view systems is found to grow when it comes to its strategic importance.