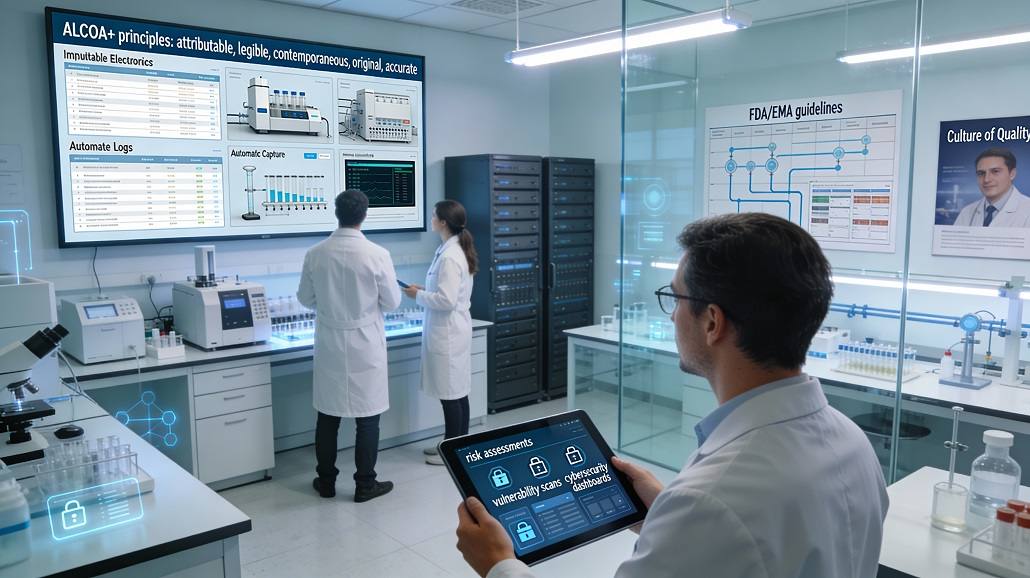
In the world of pharmaceuticals, the data is just as important as the drug itself. Without reliable, accurate information, even the most promising clinical trial results are worthless. This is why data integrity in pharmaceutical labs has become a central focus for researchers, quality assurance professionals, and regulatory agencies alike. As labs move toward more digital and automated environments, the strategies for protecting information must also evolve. Maintaining the trust of the scientific community and the safety of patients depends on a rigorous, multi-layered approach to data management.
Defining the Core Principles of Data Integrity
At its heart, data integrity in pharmaceutical labs is about ensuring that the information generated during research is a true and accurate reflection of the reality it describes. This is often summarized by the ALCOA+ acronym, which sets the standard for how data should be handled. Every record must be attributable to the person or system that generated it, legible and permanent, contemporaneous (recorded at the time of the event), original, and accurate. In the context of modern pharma labs, achieving these standards requires a combination of clear policy and advanced technological solutions.
The Shift from Manual to Digital Audit Trails
In the past, ensuring data integrity meant meticulously signing and dating paper notebooks. Today, the focus has shifted to digital audit trails. These are secure, computer-generated records that track every action taken within a software system, from logging in to modifying an experimental result. For data integrity in pharmaceutical labs, these audit trails are non-negotiable. They provide a transparent history of how a piece of data was handled, making it nearly impossible to alter results without leaving a permanent record. This transparency is a cornerstone of lab compliance.
Automated Data Capture as a Safeguard
Human error is one of the greatest threats to information quality. Manual data entry is prone to transcription mistakes, which can lead to catastrophic errors in the final analysis. To mitigate this, many pharma labs are implementing automated data capture systems. By pulling information directly from instruments like mass spectrometers or chromatography systems, researchers can ensure that the raw data is captured exactly as it was generated. This integration of smart lab data strategies eliminates the “middleman” and provides a much more robust foundation for scientific inquiry.
Building a Culture of Quality and Lab Compliance
While technology is a vital tool, data integrity in pharmaceutical labs is ultimately a human issue. No amount of software can compensate for a lack of ethical standards or poor training. To truly protect their data, organizations must foster a “culture of quality” where every employee understands the importance of honesty and accuracy. This involves regular training on laboratory best practices and a clear understanding of the consequences of data manipulation. When data integrity is seen as a shared responsibility rather than a bureaucratic hurdle, the overall quality of research improves.
Identifying and Mitigating Common Vulnerabilities
Every lab has potential weak points where data integrity could be compromised. This might be a shared password, an unmonitored instrument, or a lack of clear procedures for handling outliers. Data integrity in pharmaceutical labs requires a proactive approach to identifying these vulnerabilities through regular internal audits and risk assessments. By addressing these issues before they lead to a compliance failure, labs can maintain their standing with regulatory bodies and avoid the severe penalties associated with data misconduct.
The Role of Smart Lab Data in Compliance
The complexity of modern pharmaceutical research means that the volume of data generated is staggering. Managing this information manually is no longer feasible. Smart lab data strategies involve using intelligent systems to categorize, store, and backup data automatically. This ensures that nothing is lost and that information is always available for inspection. In a regulatory audit, the ability to quickly produce a clear, traceable data history is a significant advantage, demonstrating a commitment to the highest standards of data integrity in pharmaceutical labs.
Navigating the Global Regulatory Landscape
The requirements for data integrity are not static; they are constantly evolving as new technologies emerge. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) and the EMA (European Medicines Agency) have issued extensive guidance on how pharmaceutical labs should handle electronic records. Staying current with these regulations is a primary challenge for any research organization. By aligning their internal strategies with global laboratory best practices, labs can ensure that their data will be accepted by regulators around the world, smoothing the path to product approval.
Ensuring Data Longevity and Accessibility
Data integrity is not just about the moment a result is recorded; it is also about how that data is preserved for the future. Many pharmaceutical products have lifecycles that span decades, and the original research data must remain accessible and readable throughout that time. This requires a focus on long-term data storage strategies, including the use of non-proprietary file formats and regular migration to new hardware. Protecting data integrity in pharmaceutical labs means ensuring that the evidence for a drug’s safety and efficacy is available for as long as the product is on the market.
The Intersection of Cybersecurity and Data Integrity
In an increasingly connected world, the threat of external interference cannot be ignored. Cybersecurity is now an integral part of data integrity in pharmaceutical labs. Protecting research databases from hacking, ransomware, and unauthorized access is essential for maintaining the confidentiality and accuracy of experimental findings. This requires a robust IT infrastructure, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security updates. When smart lab data is protected by world-class cybersecurity, the integrity of the scientific process is significantly enhanced.
In conclusion, maintaining data integrity in pharmaceutical labs is a complex, ongoing challenge that requires a combination of advanced technology, rigorous policy, and a strong ethical culture. By embracing the ALCOA+ principles and implementing laboratory best practices, research facilities can ensure that their findings are both accurate and defensible. The transition to digital systems and automated workflows provides new opportunities to enhance information quality, but only if these tools are managed with precision. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to innovate, the commitment to data integrity will remain the essential foundation upon which all medical progress is built.