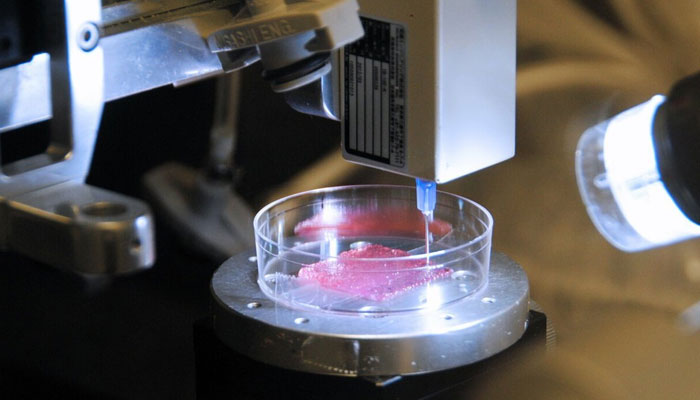
A novel 3D printed methodology for extracting stem cells from bioreactors has been created by researchers at the University of Technology, Sydney, opening the door to the possibility of high-quality, mass-produced stem cells in Australia at a cheaper price.
Due to their capacity to replenish damaged cells, stem cells hold enormous promise for the treatment of numerous illnesses and injuries, including cancer, diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis. But the existing stem cell harvesting technology is labor-intensive, time-consuming, and exorbitant.
The Australian biotechnology company Regeneus, a partner in this translational research project, is developing stem cell medicines to treat discomfort and inflammatory conditions. The first sources of mesenchymal stem cells include human bone marrow, blood, or adipose tissue. The cells are then transported to a bioreactor in the lab and combined with microcarriers to allow the cells to grow.
To remove and divide the mesenchymal stem cells from microcarriers and condense them for further processing, the innovative system comprises four micromixers, one spiral microfluidic separator, and one microfluidic concentrator. The same technique and approach, as per the researchers, can also be used to tackle other commercial bioprocessing difficulties, lowering prices and improving the quality of a selection of products that can save lives, such as CAR-T cells and stem cells.