The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) included in the UN 2030 Agenda also address the environmental, social, and economic aspects of development. In this sense, the diagnostic and healthcare industries proceed to convert the SDG Global Data agenda into development plans and policies by implementing automation, integration, digital transformation and process innovation in the laboratory. They also carry out carbon footprint reduction.
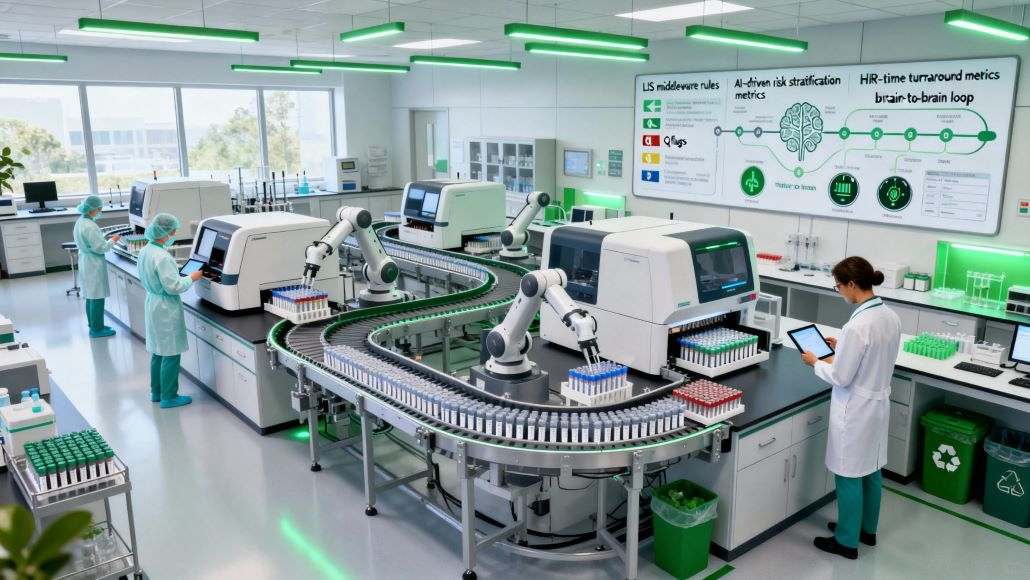
It is noteworthy that Total Lab Automation (TLA) integrates excellent healthcare via activity-based costing, automation, LEAN design, and a decrease in carbon footprint through the green lab idea. TLA also occurs to combine sustainable diagnostic innovation in lab medicine. Rapid shifts in the diagnostic industry, together with concurrent developments in lab automation and digital transformation technology in the diagnostic platforms, have sparked the emergence of methods for AI and robotic components in the regular lab process flow. It is important to note that the lab procedures have been reduced to ensure the provision of accurate and quick test results, suitable partnerships with a brain-to-brain loop, and overall improvements in patient care and safety.
The implementation of middleware, aided clinical decision-making, and the adoption of paperless workflows are crucial factors in the lab’s transformation. These factors specifically impact clinical validation, procedure efficiency, data handling and analysis, and more. AI allows the risk stratification score of clinical and laboratory data to be calculated using an expert system and evidence-based recommendations. As cost reduction requirements continue to rise, this technology’s applicability becomes more accessible.
Notably, the Lundenburg Loop idea—often called the brain-to-brain loop for laboratory testing—comes from the minds of primary care doctors who also happen to be involved in the process of choosing the lab tests and ends with the ordering physician receiving the test results in the end.
Pre-examinations, pre-examinations, tests, and post-examination procedures are essentially all that are involved in the process. To achieve process excellence within the lab workflow, the whole lab automation process is combined with the digitalization of the entire testing process.
The demand for developing a framework for sustainable technology policies and supply chain policies is quite high, as is the need to prioritize innovation and allocate resources to accelerate the growth of the IVD industry. They must also use digitalization to close the gap between supply and demand. The problems with COVID-19 indicate that concentrating on opportunities also implies pursuing opportunities while simultaneously closing the gap between supply and demand. It should be mentioned that the involvements continue to call for varying degrees of financial commitment, both in terms of immediate and long-term incremental improvements to the diagnostic care portfolio.
It is true that hospitals may continue to gain from the tech and digital transformation process in terms of both clinical and operational aspects. Complete lab automation and digitalization may improve stakeholder collaboration, improve lab and administration communication, and help hospitals and laboratories provide better results. The secret to successful and efficient illness management as well as public health management is timely communication of diagnostic test findings to doctors and other stakeholders.