The pharmaceutical landscape is currently undergoing a profound structural evolution as traditional paradigms of drug production yield to the sophisticated influence of the fourth industrial revolution. At the heart of this shift lies digital transformation in pharma manufacturing, a multi-faceted endeavor that transcends mere technological adoption to encompass a holistic reimagining of how life-saving medications are conceived, validated, and distributed. For decades, the industry was characterized by rigid, paper-based systems and siloed data architectures that, while functional for regulatory compliance, often hindered the agility and transparency required in a globalized market. Today, the integration of advanced digital tools is not merely a competitive advantage but a foundational necessity for ensuring product efficacy and patient safety.
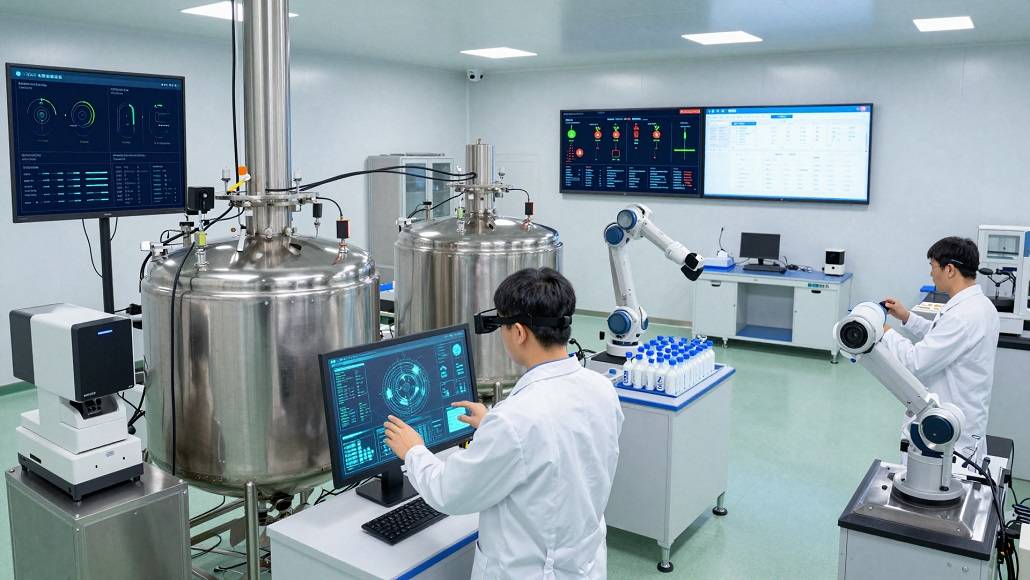
Digital transformation in pharma manufacturing begins with the digitization of the shop floor, where legacy equipment is being retrofitted with intelligent sensors and actuators. This connectivity forms the backbone of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), allowing for the seamless exchange of information between disparate machine units. When manufacturing assets can communicate in real-time, the potential for downtime is significantly mitigated through predictive maintenance algorithms that identify mechanical wear long before a failure occurs. This proactive stance is essential in an industry where even a minor deviation in temperature or pressure during the synthesis of a high-value active pharmaceutical ingredient can result in the loss of an entire batch, costing millions and delaying patient access to treatment.
Furthermore, the implementation of Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) has revolutionized the way data is recorded and audited. In a digitally transformed environment, the “golden batch” is no longer a historical outlier but a repeatable standard achieved through precise control of critical process parameters. By leveraging big data analytics, manufacturers can analyze thousands of variables simultaneously, identifying correlations that were previously invisible to human operators. This transition toward a data-driven culture ensures that every decision made on the factory floor is backed by empirical evidence, thereby strengthening the overarching quality management system.
The role of digital transformation in pharma manufacturing also extends into the realm of regulatory compliance and data integrity. Modern pharmaceutical production is governed by strict Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards, which demand a clear and immutable audit trail. Digital systems naturally facilitate this by automatically capturing timestamps, user identities, and raw data points in accordance with ALCOA+ principles (Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate, and more). By eliminating the potential for human error associated with manual transcriptions, digital platforms provide regulators with a higher level of assurance regarding the authenticity of production records. This transparency is particularly crucial as supply chains become increasingly complex and medications move across multiple international borders.
The Convergence of Process Automation and Smart Factories
As we delve deeper into the mechanics of modernization, the concept of the smart factory emerges as the ultimate realization of digital maturity. A smart factory is an interconnected ecosystem where process automation is harmonized with artificial intelligence to create a self-optimizing production environment. In such a facility, the flow of raw materials is synchronized with production schedules through advanced planning and scheduling (APS) software, minimizing inventory holding costs and reducing the risk of material expiration. This level of orchestration requires a robust digital infrastructure capable of handling high-speed data transmission and complex computational tasks without latency.
Process automation within the smart factory context is not limited to repetitive mechanical movements; it involves the automation of the cognitive processes required for quality control. Online and at-line monitoring tools, such as Near-Infrared (NIR) spectroscopy, allow for the continuous assessment of chemical compositions during the production cycle. This move toward continuous manufacturing, as opposed to traditional batch processing, is a hallmark of Industry 4.0. It enables manufacturers to adjust parameters on the fly, ensuring that the final product consistently meets predefined specifications. The resulting efficiency gains are significant, as they reduce the need for extensive end-of-line testing and quarantine periods, effectively shortening the lead time from production to patient.
Moreover, the human element within these smart factories is being augmented rather than replaced. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) technologies are increasingly utilized for training technicians on complex assembly procedures or for conducting remote maintenance with the guidance of off-site experts. By providing workers with real-time overlays of critical data and instructional guides, manufacturers can reduce the steep learning curves associated with new therapies, particularly in the burgeoning field of personalized medicine. The digital transformation in pharma manufacturing thus creates a more resilient workforce that is better equipped to navigate the complexities of modern biotechnology.
Ensuring Data Integrity and GMP Compliance through Digital Architecture
The integrity of data is the bedrock upon which the entire pharmaceutical industry rests, as it provides the proof that a drug is what it claims to be. Digital transformation in pharma manufacturing addresses the inherent vulnerabilities of physical records by introducing encrypted, cloud-based storage solutions that offer superior protection against loss or unauthorized alteration. These systems utilize advanced access controls and multi-factor authentication to ensure that only authorized personnel can interact with sensitive production data. In the event of an audit, these digital repositories allow for the rapid retrieval of information, demonstrating a level of organizational readiness that can significantly streamline the inspection process.
Adherence to GMP compliance is also simplified through automated workflow management. Digital platforms can enforce standard operating procedures (SOPs) by preventing a process from advancing to the next stage until all required checks and signatures have been completed. This “right-first-time” approach minimizes the occurrence of deviations and non-conformances, which are often the primary cause of regulatory interventions. As manufacturers embrace digital transformation in pharma manufacturing, they find that compliance becomes an integrated feature of the production process rather than an external burden to be managed separately.
Beyond the walls of the factory, the “digital thread” connects the entire product lifecycle, from initial research and development to the final patient experience. This end-to-end visibility allows for unprecedented levels of transparency in the supply chain, enabling companies to track individual vials or blisters through serialisation and blockchain technology. In the fight against counterfeit medications, this capability is invaluable, as it ensures that the medicine reaching the pharmacy shelf is authentic and has been stored within the required environmental parameters during transit.
Artificial Intelligence in Quality Assurance and Process Control
One of the most promising frontiers of digital transformation in pharma manufacturing is the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in quality assurance. Traditional quality control relies heavily on retrospective testing, where samples are pulled from finished batches and analyzed in a lab. If a failure is detected, the entire batch must often be discarded. AI changes this reactive model by providing predictive insights during the manufacturing process. Machine learning models can be trained on vast historical datasets to recognize the subtle early-warning signs of a process drift. By identifying these patterns, the system can recommend immediate corrective actions, such as adjusting flow rates or temperatures, to bring the process back into the optimal range.
This transition toward “Real-Time Release Testing” (RTRT) represents a paradigm shift in pharmaceutical production. Instead of waiting days or weeks for lab results, manufacturers can release products almost immediately after production, provided that the digital sensors and AI models confirm that all critical quality attributes have been met. This speed is essential for biologics and radiopharmaceuticals, which often have very short shelf lives. Furthermore, AI-driven visual inspection systems are now capable of detecting microscopic defects in vials and syringes with a degree of accuracy and speed that far exceeds human capabilities. These systems never tire and maintain a constant level of vigilance, ensuring that only the highest quality products reach the patient.
Overcoming Integration Challenges with Legacy Systems
While the benefits of digital transformation in pharma manufacturing are clear, the path to implementation is often fraught with technical and organizational challenges. Many pharmaceutical companies operate with a patchwork of legacy equipment that was never designed for digital connectivity. Bridging the gap between 20-year-old machinery and modern cloud-based analytics requires a strategic approach to data ingestion and protocol translation. Edge computing devices are frequently used to collect data from these older machines, process it locally, and then transmit it in a standardized format to central systems. This hybrid approach allows manufacturers to realize the benefits of Industry 4.0 without the prohibitive cost of replacing every asset in their fleet.
Organizational culture also plays a pivotal role in the success of digital initiatives. Resistance to change is a common hurdle, as long-tenured employees may be skeptical of new digital workflows or fear that automation will make their roles redundant. Overcoming this requires a strong commitment from leadership to foster a culture of continuous learning and digital literacy. By demonstrating that digital tools are intended to empower workers and remove the drudgery of manual data entry, companies can build the internal consensus necessary for a smooth transition. Training programs that focus on data interpretation and system management are essential for preparing the workforce for the digital age.
Cybersecurity and the Future of Networked Production
With the rise of interconnected systems, the importance of cybersecurity in pharmaceutical manufacturing cannot be overstated. As the physical and digital worlds merge, the vulnerability to cyberattacks increases, making the protection of intellectual property and production systems a top priority. Digital transformation in pharma manufacturing therefore includes the deployment of sophisticated network monitoring and threat detection tools designed to safeguard the integrity of the manufacturing process. A robust cybersecurity posture ensures that the digital benefits of speed and efficiency are not compromised by malicious actors.
The transition toward personalized medicine, such as Cell and Gene Therapy (CGT), further underscores the need for digital agility. These therapies require a “vein-to-vein” digital tracking system that manages the unique logistics of handling patient-specific materials. Digital platforms coordinate the collection of patient cells, their transport to a manufacturing facility, the complex processing required, and their eventual return for infusion. Without the high-fidelity data tracking provided by digital transformation in pharma manufacturing, the delivery of these highly complex and life-saving treatments would be practically impossible at scale.
Environmental sustainability is another area where digital maturity is yielding significant dividends. By optimizing energy consumption and reducing waste through precise process control, digitalized facilities are significantly lowering their carbon footprint. Smart lighting, HVAC systems controlled by occupancy sensors, and high-efficiency motors all contribute to a more sustainable manufacturing model. In this regard, digital transformation is not just about profit and efficiency; it is a critical component of the industry’s commitment to environmental stewardship and corporate social responsibility.
In conclusion, the journey toward a fully digitalized pharmaceutical manufacturing landscape is a continuous process of learning and adaptation. As technologies such as quantum computing and advanced robotics continue to mature, the potential for further innovation will only grow. The cornerstone of this future will remain the ability to integrate disparate data sources into a cohesive, actionable narrative that prioritizes quality and safety. As manufacturers continue to invest in digital transformation in pharma manufacturing, they are not just upgrading their machines; they are building the infrastructure of a healthier world, characterized by more accessible, affordable, and effective healthcare solutions for everyone.