Accelerating Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical Innovation through America’s AI Action Plan
America’s AI Action Plan, unveiled in July 2025, lays out a comprehensive strategy to propel the United States to the forefront of global AI leadership. Within its three pillars—innovation, infrastructure, and international diplomacy—the Plan contains transformative policies tailored to the pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical industries. By harnessing AI-driven breakthroughs in drug discovery, manufacturing, data sharing, workforce development, and biosecurity, the Plan charts a path toward faster, safer, and more cost-effective development of new therapies.
AI-Enabled Drug Discovery and Automated Laboratories
Central to the Plan’s vision is the use of AI to revolutionise early-stage research. Traditional drug discovery, often a years-long, high-cost endeavour, will be dramatically accelerated by AI tools capable of:
- Predicting protein structures and binding interactions with unprecedented speed and accuracy
- Designing candidate molecules through generative models trained on vast chemical libraries
- Prioritizing compounds most likely to succeed in preclinical testing
To translate these AI predictions into real-world breakthroughs, the Plan directs major investments in automated cloud-enabled laboratories. These next-generation facilities—built through public-private partnerships involving the National Science Foundation, the Department of Energy, and leading biopharmaceutical firms—will integrate robotic experimentation platforms, high-throughput screening, and AI-driven hypothesis generation. By closing the loop between in silico design and in vitro validation, these “lab clouds” aim to reduce the time from target identification to candidate selection from years to months.
Building High-Quality Biomedical Datasets
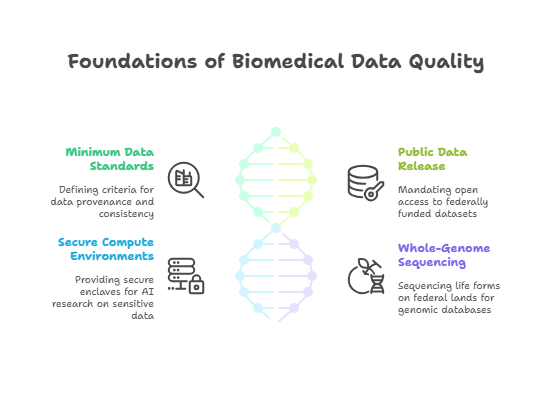
Machine learning models thrive on data. Yet the biopharmaceutical sector’s data landscape has long been fragmented across proprietary silos. The AI Action Plan tackles this bottleneck by:
- Establishing Minimum Data Quality Standards
A national committee will define criteria for data provenance, annotation consistency, and interoperability across modalities—genomic, proteomic, clinical trial, and real-world evidence. - Mandating Public Release of Federally Funded Datasets
Investigators receiving NIH and National Science Foundation grants must publish non-sensitive, de-identified datasets in open repositories, ensuring broader access for AI model training. - Creating Secure Compute Environments
To protect proprietary or sensitive data, the Plan funds secure enclaves where researchers can run AI algorithms on restricted datasets without direct data export. - Whole-Genome Sequencing on Federal Lands
A bold initiative to sequence all life forms on public lands will generate massive genomic databases, fuelling next-generation biopharma AI models for target discovery and biomarker identification.
By weaving these efforts together, the Plan envisions a federated data ecosystem where academic laboratories, biotech startups, and large pharma can collaborate on shared AI challenges while safeguarding patient privacy and intellectual property.
Biosecurity and Safe Biological Design
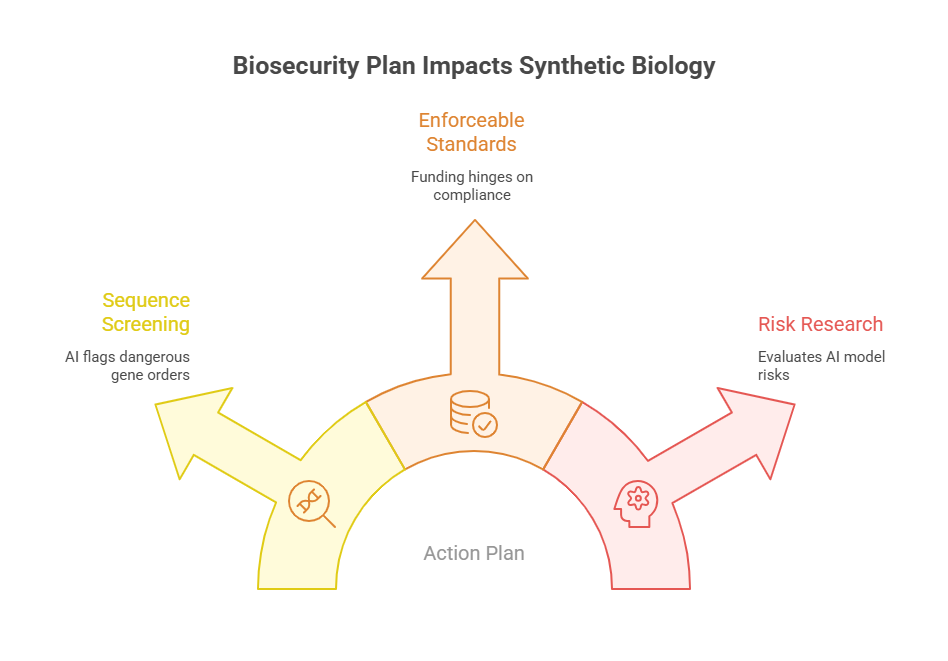
AI’s power to design novel genetic sequences raises both medical promise and biosecurity concerns. The Action Plan introduces strict controls on synthetic biology tools used in drug manufacture and vaccine development:
- Mandatory Sequence Screening
All companies offering gene synthesis services must deploy robust AI-based screening to flag orders that resemble dangerous pathogens or toxin genes. Real-time alerts and data sharing among providers will prevent malicious misuse. - Enforceable Standards
Instead of voluntary guidelines, federal funding now hinges on compliance with detailed biosecurity protocols. Organisations failing to meet these will lose access to grants and procurement opportunities. - Research on Frontier Models’ Risks
Through NIST and the Department of Commerce, the Plan mandates evaluations of emerging AI models for their potential to generate harmful biological designs, with findings informing regulation.
These measures ensure that as the biopharma sector accelerates vaccine and therapeutic development through AI, it does so within a fortified safety framework.
Next-Generation Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing
Manufacturing biologics—antibodies, cell therapies, and complex proteins—requires stringent process controls and continuous innovation. The AI Action Plan directs targeted funding to integrate AI for:
- Process Optimization
Machine learning models will analyse real-time bioreactor sensor data to adjust parameters—pH, temperature, nutrient feed—maximising yield and consistency. - Predictive Maintenance
AI-driven monitoring of equipment health will preemptively flag maintenance needs, reducing downtime and production delays. - Quality Control Automation
Computer vision systems will inspect vials and final product batches for visual defects, enhancing release testing speed and reliability.
Support comes through expanded Small Business Innovation Research grants and Title III Defense Production Act authorities, allowing rapid scale-up of modular, AI-enabled biomanufacturing facilities. By fostering public-private partnerships, the Plan aims to anchor advanced biologics production on U.S. soil, securing supply chains for critical therapeutics.
Workforce Development for AI-Driven Biopharma
Deploying AI across R&D and manufacturing requires a workforce fluent in data science, machine learning, and bioengineering. The Plan establishes:
- An AI Biopharma Training Hub under the Department of Labor, partnering with community colleges and research institutions to deliver certificates in AI-augmented drug development workflows.
- Tax guidance clarifying that AI upskilling programs qualify for educational assistance credits, incentivising employers to cover training costs for lab technicians, process engineers, and regulatory specialists.
- A Rapid Retraining Pilot to transition professionals displaced by automation into high-value roles such as AI model validation, clinical data analysis, and regulatory compliance.
By bridging the skills gap, these initiatives ensure that U.S. biopharma firms have the talent pipeline needed to fully leverage AI’s potential.
Advancing AI Interpretability and Regulatory Trust
One barrier to regulatory acceptance of AI in drug approvals is model opacity. To address this, the Plan calls for:
- A DARPA-led program to develop interpretable AI architectures that provide mechanistic insights into molecular design decisions.
- Joint AI hackathons where academia and industry teams stress-test models for robustness, adversarial resilience, and explainability.
- NIST-sponsored guidelines on AI evaluation metrics tailored to biopharmaceutical use cases, facilitating transparent communication with the FDA.
These efforts aim to build trust between AI developers and regulators, smoothing the path for AI-designed therapeutics to enter clinical trials.
Global Leadership and Export Controls
The U.S. seeks to establish its AI-driven biopharma innovations as the global gold standard. The Plan includes:
- Export of American AI Platforms for drug discovery to allied nations, combined with joint research initiatives.
- Tightening of Export Controls on high-performance compute hardware crucial for training large biological foundation models, preventing potential misuse by adversarial states.
By balancing open collaboration with strategic controls, the Plan ensures American biopharma AI remains both influential and secure on the world stage.
Conclusion
America’s AI Action Plan offers a robust blueprint for transforming the pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical industries. Through investments in automated labs, data infrastructure, biosecurity, manufacturing modernization, workforce training, and interpretability research, it accelerates the journey from molecule to medicine. By anchoring these advances in rigorous safety and regulatory frameworks, the United States is poised to lead a new era of AI-enabled therapeutics—delivering faster cures, lowering costs, and safeguarding public health on a global scale.