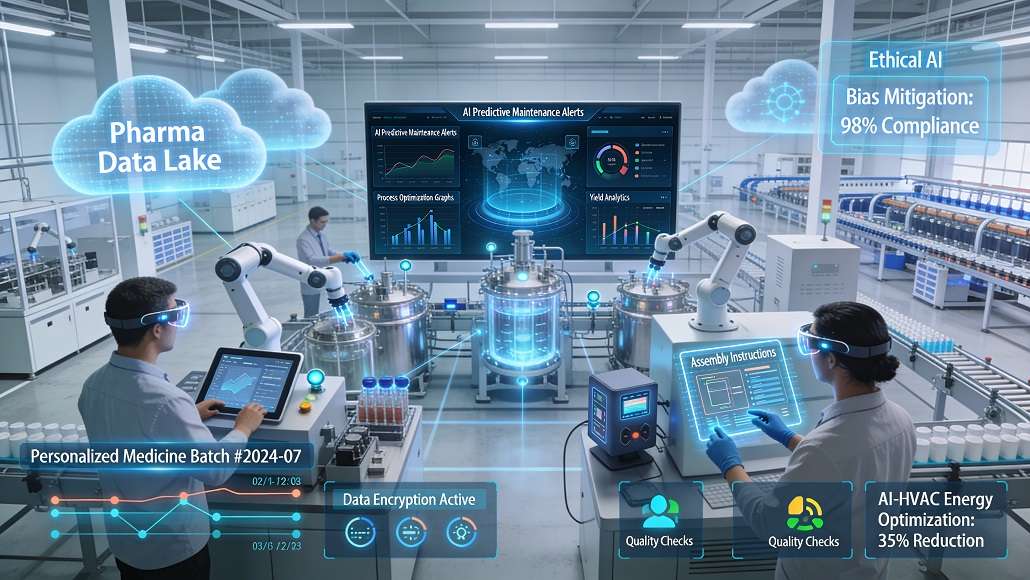
The concept of the “smart factory” has evolved from a futuristic vision into a tangible reality that is redefining the global pharmaceutical industry. At its core, smart factories driving pharma Industry 4.0 represent the convergence of physical manufacturing assets with advanced digital technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data analytics. This integration creates a highly connected and intelligent production environment where data flows seamlessly across the entire value chain, enabling unprecedented levels of agility, efficiency, and quality control. For pharmaceutical companies, the transition to smart manufacturing is not just an operational upgrade; it is a strategic necessity for competing in an era of personalized medicine and increasing regulatory complexity.
The foundation of smart factories driving pharma Industry 4.0 is connectivity. In a traditional factory, machines often operate in isolation, with data trapped in “silos” that are difficult to access or analyze. In a smart factory, every piece of equipment from the high-speed tablet press to the environmental monitoring sensors is connected to a central digital backbone. This connectivity allows for real-time visibility into the status of the entire production floor. Operators and managers can monitor performance metrics, identify bottlenecks, and respond to deviations instantaneously through intuitive dashboards. This “single source of truth” ensures that everyone in the organization is working with the same data, fostering a culture of transparency and collaboration.
The Power of AI and Predictive Analytics in Manufacturing
A defining characteristic of smart factories driving pharma Industry 4.0 is the use of artificial intelligence to optimize production processes. AI algorithms can analyze the vast amounts of data generated by IoT sensors to identify patterns and correlations that are invisible to the human eye. One of the most valuable applications is predictive maintenance. By analyzing vibration, temperature, and power consumption data, AI can predict when a machine is likely to fail and schedule maintenance before a breakdown occurs. This minimizes unplanned downtime and ensures that the manufacturing process remains in a constant state of readiness, which is crucial for maintaining a steady supply of essential medications.
Furthermore, AI-driven process optimization is helping manufacturers achieve higher yields and consistent quality. Machine learning models can be trained to recognize the “ideal” conditions for a particular manufacturing step and automatically adjust parameters to maintain that state. For instance, in the complex process of lyophilization (freeze-drying), AI can optimize the drying cycles to reduce energy consumption and prevent product degradation. This level of autonomous decision-making is the hallmark of the smart factory, where the system is not just monitoring the process but actively managing it to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Edge Computing and Real-Time Data Processing
As the volume of data generated by smart factories continues to explode, the role of edge computing is becoming increasingly critical. Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source at the level of the machine or the production line rather than sending it all to a centralized cloud. This reduces latency, which is essential for real-time control applications where even a millisecond of delay can affect the quality of a high-value batch. Smart factories driving pharma Industry 4.0 utilize edge devices to perform initial data filtering and analysis, ensuring that only the most relevant information is transmitted to the cloud for long-term storage and higher-level analytics.
This decentralized approach also enhances the cybersecurity and resilience of the manufacturing network. By processing sensitive data locally, companies can reduce the risk of interception during transmission and maintain core operations even if the connection to the central cloud is temporarily interrupted. As edge technology continues to mature, we can expect to see even more sophisticated AI models being deployed directly onto the factory floor, allowing for even greater levels of autonomous and real-time process management.
Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience and Customer Centricity
The impact of smart factories driving pharma Industry 4.0 extends far beyond the four walls of the manufacturing facility. By integrating production data with supply chain management systems, companies can achieve end-to-end visibility from raw material sourcing to the final patient delivery. This “digital thread” allows for more accurate forecasting and more responsive production scheduling. If a shipment of raw materials is delayed, the smart factory can automatically reconfigure its production lines to focus on other products, minimizing the impact on the overall supply chain. This resilience is particularly important in a world where geopolitical instability and climate events can disrupt global logistics.
Moreover, smart manufacturing enables a more customer-centric approach to pharmaceutical production. The rise of personalized medicine, such as “CAR-T” cell therapies, requires a manufacturing model that is tailored to the needs of individual patients. Smart factories are uniquely suited for this “batch size of one” production, as their digital infrastructure can manage the complex logistics and unique processing requirements of each personalized dose. By automating the tracking and validation of patient-specific materials, smart factories driving pharma Industry 4.0 are making these life-saving therapies more accessible and affordable for those who need them most.
Human-Machine Collaboration and the Future Workforce
A common misconception is that the rise of smart factories will lead to the total displacement of human workers. In reality, the future of manufacturing lies in the collaboration between humans and machines. In smart factories driving pharma Industry 4.0, workers are being empowered with digital tools that augment their capabilities. Collaborative robots (cobots) can handle repetitive or hazardous tasks, allowing human employees to focus on more complex activities such as process design, data analysis, and quality assurance. Augmented reality (AR) headsets provide technicians with real-time instructions and data overlays, reducing the risk of error and accelerating the training process for new hires.
This shift requires a significant focus on upskilling and reskilling the workforce. The “pharmaceutical worker of the future” will need a combination of domain expertise and digital literacy. Companies must invest in training programs that teach employees how to interact with AI systems, interpret data analytics, and manage complex digital workflows. By fostering a culture of continuous learning, pharmaceutical companies can ensure that their most valuable asset their people is prepared to thrive in the digital age. The successful integration of technology and human talent is the ultimate key to realizing the full potential of the smart factory.
Ethical AI and Data Governance in Pharma 4.0
As artificial intelligence takes on a more prominent role in decision-making, the importance of ethical AI and robust data governance cannot be overstated. Smart factories driving pharma Industry 4.0 must ensure that their algorithms are transparent, explainable, and free from bias. This is particularly important in a regulated industry like pharmaceuticals, where the safety and efficacy of products are paramount. Manufacturers must be able to demonstrate to regulators exactly how an AI system reached a particular decision, especially when it affects critical quality attributes.
Furthermore, the management of the vast datasets generated by smart factories requires a sophisticated data governance framework. This includes ensuring data integrity, protecting patient privacy, and managing intellectual property in a highly connected ecosystem. As companies share more data with supply chain partners and technology providers, the ability to maintain a secure and compliant data environment will be a major differentiator. By building trust through transparent and ethical data practices, pharmaceutical companies can unlock the full value of the Industry 4.0 revolution.
In conclusion, the journey toward smart factories driving pharma Industry 4.0 is a transformative process that is reshaping the very fabric of the pharmaceutical industry. By leveraging the power of connectivity, AI, and data analytics, manufacturers are building a more efficient, resilient, and patient-centric production ecosystem. While the challenges of implementation are significant, the rewards in terms of improved quality, reduced costs, and faster access to life-saving medicines are even greater. As the technology continues to evolve, the smart factory will remain the primary engine of innovation, ensuring that the pharmaceutical industry can meet the healthcare challenges of the 21st century with precision and purpose.
Sustainability and the Smart Factory of the Future
The integration of sustainability goals into the smart factory framework is a defining trend of the Industry 4.0 era. Smart factories driving pharma Industry 4.0 are uniquely positioned to minimize their environmental impact through the intelligent management of resources. By utilizing IoT sensors to monitor energy and water consumption in real-time, these facilities can identify areas of waste and implement automated strategies for conservation. For example, AI-driven HVAC systems can adjust heating and cooling based on the occupancy and heat-load of a specific production area, significantly reducing energy usage. Furthermore, the precise process control enabled by smart manufacturing reduces the occurrence of batch failures, which are a major source of waste in the pharmaceutical industry. By ensuring that every batch is produced correctly the first time, smart factories are contributing to a more circular and resource-efficient economy. As the industry faces increasing pressure to demonstrate its environmental credentials, the smart factory will be the primary vehicle for achieving deep decarbonization and sustainability. This holistic approach to manufacturing ensures that smart factories driving pharma Industry 4.0 are not just about profit and efficiency; they are about building a healthier and more sustainable world for future generations.
In addition to the environmental benefits, the smart factory model also enhances the social sustainability of the pharmaceutical industry. By providing workers with advanced digital tools and ergonomic support, these facilities are creating a safer and more rewarding work environment. The use of cobots to handle heavy or repetitive tasks reduces the risk of workplace injuries, while AR training programs ensure that employees are well-prepared for the complexities of modern manufacturing. This focus on human-centric technology is essential for building a resilient and skilled workforce that is capable of driving the industry forward. As we move further into the 21st century, the ability to balance the needs of people, planet, and profit will be the hallmark of a successful pharmaceutical company. The smart factory is the engine that will power this balanced growth, ensuring that the pursuit of human health is always aligned with the broader goals of social and environmental responsibility. The future is smart, and the future is sustainable.