The Foundation of Temperature-Controlled Pharmaceutical Logistics
The pharmaceutical industry operates under stringent regulations where maintaining product integrity throughout the supply chain is paramount to patient safety and therapeutic efficacy. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for handling temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical products represent the backbone of cold chain management, ensuring that critical medications, vaccines, and biologics maintain their therapeutic properties from manufacturing to patient administration.
Temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical products encompass a diverse range of therapeutic agents, including vaccines requiring 2-8°C storage, insulin formulations, monoclonal antibodies, gene therapies, and ultra-cold chain products like certain COVID-19 vaccines requiring storage below -70°C. The complexity of managing these products across multiple transit modes necessitates comprehensive SOPs that address every aspect of the cold chain continuum.
The financial implications of temperature excursions in pharmaceutical logistics are staggering, with studies indicating that temperature deviations can result in 25% of vaccines becoming ineffective before reaching their destination. This underscores the critical importance of implementing robust SOPs that encompass all facets of temperature-controlled transportation and storage.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance Standards
Pharmaceutical cold chain SOPs must align with multiple regulatory frameworks, including Good Distribution Practices (GDP) established by the European Union, FDA regulations under 21 CFR Part 211, and World Health Organization guidelines for time and temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical products. These regulations mandate that pharmaceutical companies maintain documented evidence of temperature control throughout the entire supply chain.
The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines, particularly ICH Q1A for stability testing, provide fundamental requirements for establishing temperature parameters and monitoring protocols. Companies must demonstrate through validated SOPs that their temperature-controlled systems can consistently maintain products within specified temperature ranges under various environmental conditions and transportation scenarios.
Good Distribution Practice Requirements
GDP guidelines establish comprehensive requirements for temperature-controlled storage and distribution, emphasizing the need for validated systems, trained personnel, and documented procedures. SOPs must address temperature monitoring with accuracy of ±0.5°C or better, continuous recording systems, and alarm systems for temperature excursions.
The GDP framework requires that SOPs cover temperature mapping of storage facilities, qualification of thermal packaging systems, and validation of transportation routes. These procedures must be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in products, routes, or environmental conditions.
Multi-Modal Transportation Protocols
Developing SOPs for pharmaceutical cold chain across multiple transit modes requires understanding the unique challenges and requirements of road, air, sea, and rail transportation. Each mode presents distinct environmental conditions, handling procedures, and risk profiles that must be addressed through specific protocols.
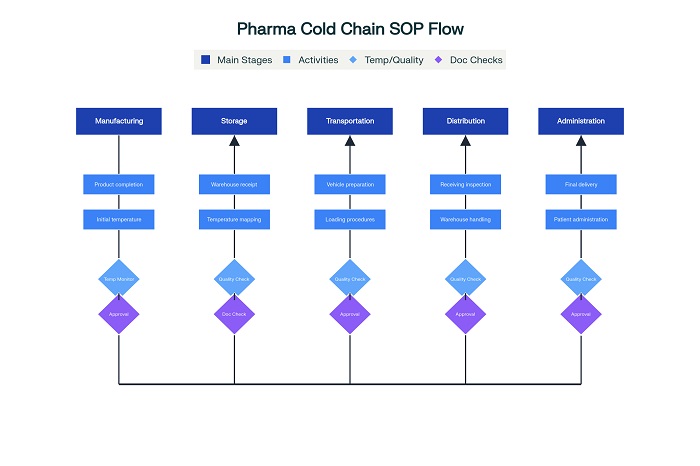
Road transportation protocols must address vehicle qualification, driver training, route optimization, and contingency planning for mechanical failures or delays. SOPs should specify pre-trip inspections of refrigeration systems, temperature monitoring equipment calibration, and documentation requirements for temperature logs throughout transit.
Air Transport Specifications
Air transportation of temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals requires adherence to International Air Transport Association (IATA) Temperature Control Regulations and specific SOPs for airport handling. These procedures must address tarmac exposure times, ground handling protocols, and coordination between multiple stakeholders in the air cargo supply chain.
The IATA guidelines specify maximum exposure times for different temperature categories, with vaccines typically limited to 30 minutes of ambient temperature exposure during transfers. SOPs must detail procedures for minimizing these exposure periods and maintaining temperature integrity during aircraft loading and unloading operations.
Maritime and Rail Considerations
Sea and rail transportation present unique challenges for temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals, including extended transit times, limited monitoring capabilities, and potential for extreme weather exposure. SOPs must address container qualification, monitoring system redundancy, and protocols for handling temperature excursions during extended voyages.
Maritime SOPs require special attention to humidity control, as sea transport environments can experience significant moisture variations that may affect packaging integrity and product stability. Rail transport protocols must consider vibration impacts on temperature-sensitive products and monitoring equipment.
Temperature Monitoring and Documentation Systems
Comprehensive SOPs must establish detailed protocols for temperature monitoring throughout the cold chain, incorporating both continuous monitoring systems and manual verification procedures. Modern IoT-enabled monitoring solutions provide real-time data collection and alert capabilities, but SOPs must also address backup systems and manual procedures for system failures.
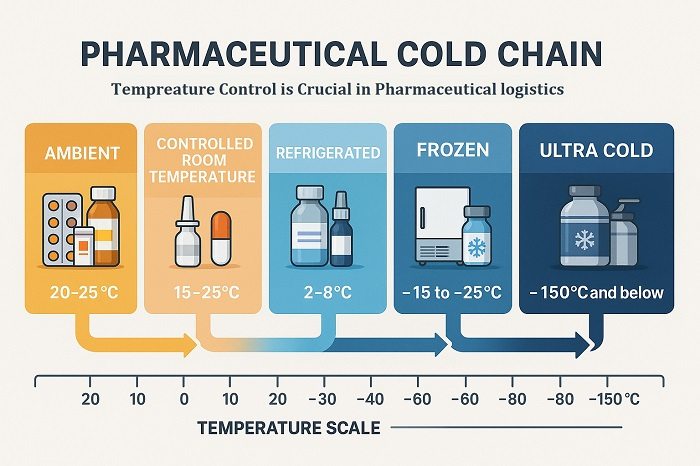
Temperature monitoring SOPs should specify calibration schedules for all monitoring equipment, data logging requirements, and procedures for investigating temperature excursions. The documentation must be sufficient to demonstrate regulatory compliance and support product release decisions upon receipt.
Real-Time Monitoring Protocols
Real-time monitoring systems enable proactive intervention when temperature excursions occur, but SOPs must define clear escalation procedures and response protocols. These procedures should specify who receives alerts, timeframes for response, and corrective actions to be taken based on the severity and duration of temperature deviations.
SOPs must also address data integrity requirements for electronic monitoring systems, including user access controls, audit trails, and data backup procedures to ensure regulatory compliance and traceability.
Thermal Packaging Systems and Qualification
Thermal packaging selection and qualification represent critical components of temperature-controlled pharmaceutical SOPs. The procedures must address packaging system design qualification (DQ), operational qualification (OQ), and performance qualification (PQ) as defined by International Safe Transit Association (ISTA) and Parenteral Drug Association (PDA) guidelines.
Packaging qualification SOPs must specify testing protocols for different environmental conditions, seasonal variations, and transportation durations. The qualification process should include thermal mapping studies, accelerated aging tests, and real-world distribution testing to validate packaging performance.
Passive vs. Active Packaging Systems
SOPs must differentiate between passive thermal packaging systems that rely on phase change materials and insulation, and active systems that incorporate powered cooling or heating elements. Each system type requires specific handling procedures, pre-conditioning protocols, and monitoring requirements.
Passive systems require SOPs for conditioning temperatures and durations before use, while active systems need procedures for battery management, system startup, and failure contingencies. The selection criteria between systems should be documented based on product requirements, transit duration, and environmental conditions.
Personnel Training and Competency Management
Effective implementation of temperature-controlled pharmaceutical SOPs requires comprehensive training programs for all personnel involved in the cold chain. Training protocols must address role-specific responsibilities, emergency procedures, and regulatory compliance requirements.
SOPs should establish competency assessment criteria for different roles, including cold chain managers, warehouse personnel, drivers, and quality assurance staff. Training documentation must demonstrate that personnel understand their responsibilities and can execute procedures correctly under various conditions.
Emergency Response Training
Emergency response training represents a critical component of cold chain SOPs, addressing procedures for temperature excursions, equipment failures, and unexpected delays. Personnel must understand decision-making protocols, communication procedures, and corrective actions to minimize product risk.
Training programs should include simulation exercises that test personnel response to various emergency scenarios, ensuring they can execute SOPs effectively under pressure and make appropriate decisions to protect product integrity.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Comprehensive SOPs must incorporate risk assessment methodologies that identify potential threats to temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical products throughout the supply chain. These assessments should consider environmental factors, equipment reliability, human error potential, and external disruptions such as severe weather or transportation delays.
Risk mitigation strategies embedded in SOPs should include contingency planning for various failure scenarios, backup system requirements, and decision trees for handling temperature excursions. The procedures must balance product safety considerations with economic factors while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Seasonal Variation Management
SOPs must address seasonal variations in environmental conditions and their impact on temperature-controlled pharmaceutical distribution. Summer and winter protocols may require different thermal packaging solutions, modified transportation routes, and adjusted monitoring parameters.
Seasonal SOPs should specify when to implement different packaging configurations, how to adjust monitoring thresholds, and procedures for managing extreme weather conditions that may affect transportation schedules or equipment performance.
Quality Management and Continuous Improvement
Temperature-controlled pharmaceutical SOPs must incorporate quality management principles that ensure continuous improvement and adaptation to changing requirements. Regular review and updating of procedures based on performance data, regulatory changes, and technological advances are essential for maintaining effectiveness.
Quality metrics embedded in SOPs should include key performance indicators for temperature compliance, on-time delivery, and product integrity. These metrics enable identification of improvement opportunities and demonstration of system performance to regulatory authorities and customers.
The implementation of comprehensive SOPs for temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical products across multiple transit modes requires careful consideration of regulatory requirements, technological capabilities, and operational realities. Success depends on thorough documentation, rigorous training, and continuous monitoring of system performance to ensure that critical medications reach patients with their therapeutic properties intact. Organizations that invest in robust SOPs and their proper implementation will be better positioned to meet the growing demands of the temperature-controlled pharmaceutical market while maintaining the highest standards of patient safety and regulatory compliance.