Smart Labeling Enhancing Pharma Supply Chain Transparency
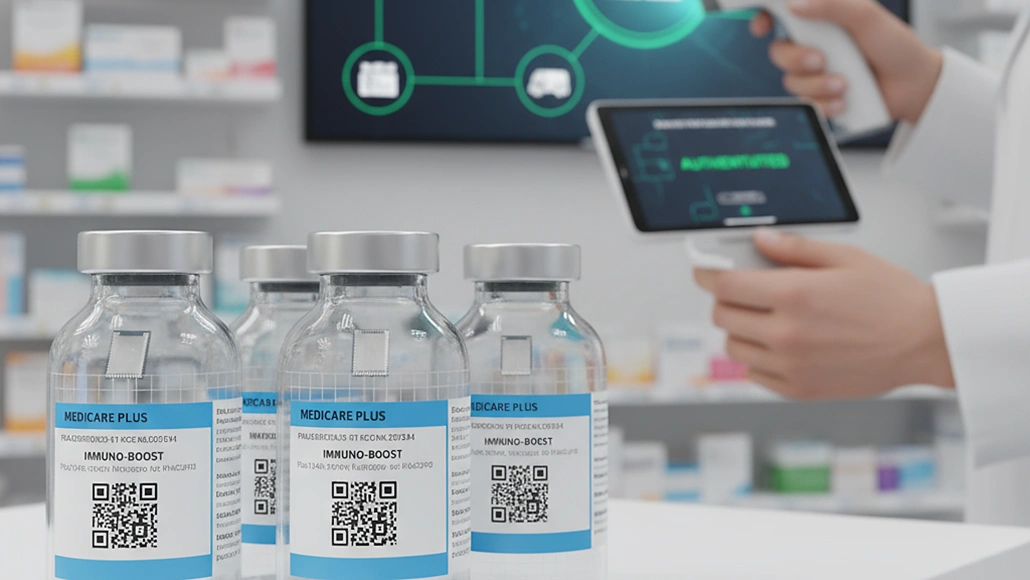
The pharmaceutical industry has undergone a revolutionary transformation through the implementation of smart labeling in pharma, fundamentally changing how medications are tracked, authenticated, and managed throughout complex global supply chains. These intelligent labeling solutions integrate advanced technologies including Radio Frequency Identification, Near Field Communication, and sophisticated barcode systems to create comprehensive traceability networks that enhance patient safety, support regulatory compliance, and optimize supply chain efficiency.
The Digital Revolution in Pharmaceutical Labeling
Smart labels represent a paradigm shift from traditional passive labeling approaches to dynamic, interactive systems that store and transmit critical product information throughout the pharmaceutical supply chain. The global smart labels market for healthcare and pharmaceutical industries was valued at USD 2.48 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 17.5 percent through 2034, reflecting the rapidly increasing adoption of intelligent labeling technologies across pharmaceutical operations.
The rise of smart pharmaceutical labeling has been driven by stringent regulatory requirements, growing concerns about counterfeit medications, and the increasing complexity of global pharmaceutical supply chains. These intelligent systems enable real-time tracking and authentication that were impossible with traditional labeling approaches, providing unprecedented visibility into product movement and handling throughout distribution networks.
Contemporary smart labeling solutions incorporate multiple technologies simultaneously, creating hybrid systems that provide redundant authentication methods while supporting diverse user requirements across different points in the supply chain. These multi-technology approaches ensure compatibility with existing infrastructure while providing enhanced security and functionality that address evolving pharmaceutical industry needs.
Advanced RFID Technologies Transforming Track and Trace Capabilities
Radio Frequency Identification technology has emerged as a cornerstone of smart pharmaceutical labeling, providing contactless identification and data transmission capabilities that support high-speed automated processing and comprehensive supply chain visibility. RFID systems can store substantial amounts of product information while enabling real-time updates and modifications throughout the product lifecycle.
Pharmaceutical-grade RFID labels incorporate specialized designs that accommodate the challenging environments encountered in pharmaceutical distribution, including temperature extremes, moisture exposure, and chemical resistance requirements. These robust labels maintain functionality throughout cold chain distribution while providing reliable data transmission under diverse operating conditions.
Ultra-High Frequency RFID systems enable long-range reading capabilities that support automated inventory management and supply chain tracking without direct handling or line-of-sight requirements. These systems can simultaneously read multiple products during shipping and receiving operations, dramatically improving operational efficiency while maintaining comprehensive tracking accuracy.
Passive RFID labels provide cost-effective solutions for high-volume pharmaceutical applications, utilizing power from reader devices to transmit stored information without requiring internal batteries. These systems offer extended operational life while maintaining affordability for single-use pharmaceutical packaging applications.
Near Field Communication Enabling Consumer Engagement
Near Field Communication technology provides smartphone-accessible smart labeling solutions that enable consumers and healthcare providers to verify product authenticity and access detailed medication information through simple tap interactions. NFC-enabled pharmaceutical packaging transforms traditional product containers into interactive information sources that support patient education and medication management.
Temperature monitoring capabilities integrated into NFC labels provide real-time environmental data that helps ensure product quality and therapeutic effectiveness. These smart labels can alert users when medications have been exposed to conditions outside specified parameters, providing additional assurance of product integrity and safety.
Consumer engagement features enabled through NFC technology include access to instructional videos, dosage reminders, and educational content that support proper medication use and improved adherence. These interactive capabilities transform pharmaceutical packaging into comprehensive patient support systems that extend beyond basic product containment.
Healthcare provider applications of NFC technology enable rapid product verification, batch information access, and integration with electronic health records that support clinical decision-making and regulatory compliance. These professional-grade features provide healthcare facilities with enhanced product information and authentication capabilities.
Serialization and Data Matrix Integration
Pharmaceutical serialization through two-dimensional data matrix codes has become a fundamental requirement for regulatory compliance and supply chain security across global markets. These standardized coding systems enable unique product identification while supporting automated reading and verification throughout distribution networks.
GS1 standards provide the technical framework for pharmaceutical serialization, ensuring interoperability among different manufacturers, distributors, and healthcare providers worldwide. These standardized approaches enable seamless data exchange while supporting diverse regulatory requirements across different markets and jurisdictions.
Aggregation capabilities link individual pharmaceutical units with shipping containers and pallets, creating hierarchical tracking systems that support supply chain optimization and regulatory compliance. These multi-level tracking systems enable comprehensive visibility from individual dose units through bulk distribution packages.
Verification systems enable real-time authentication of serialized pharmaceutical products, providing immediate confirmation of product legitimacy and supply chain integrity. These verification capabilities support both automated processing systems and manual verification procedures used by healthcare providers and regulatory authorities.
Integration with Supply Chain Management Systems
Smart labeling technologies integrate seamlessly with enterprise resource planning and supply chain management systems to provide comprehensive visibility and control over pharmaceutical distribution operations. This integration enables real-time decision-making that optimizes inventory management while ensuring product quality and regulatory compliance throughout the supply chain.
Automated inventory management through smart labeling systems enables real-time tracking of product location, quantity, and status throughout distribution networks. These systems can automatically update inventory records, trigger reorder notifications, and provide comprehensive reporting that supports supply chain optimization and regulatory compliance.
Cold chain monitoring integration enables continuous temperature and environmental tracking that ensures product quality throughout distribution of temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals. Smart labels can provide real-time alerts when products are exposed to conditions outside specified parameters, enabling immediate corrective action to preserve product integrity.
Recall management capabilities enhanced through smart labeling enable rapid identification and isolation of affected products when quality issues or safety concerns arise. These systems can quickly identify the location and status of specific product lots while supporting comprehensive recall documentation and regulatory reporting requirements.
Regulatory Compliance and Documentation Excellence
Smart labeling systems provide automated documentation capabilities that exceed traditional manual record-keeping methods while ensuring compliance with FDA, EMA, and other regulatory standards for pharmaceutical distribution. These systems create comprehensive audit trails that document product handling and environmental exposure throughout the supply chain.
Serialization compliance requirements mandated by regulations such as the Drug Supply Chain Security Act and Falsified Medicines Directive are addressed through standardized smart labeling approaches that ensure consistent implementation across diverse markets and supply chain partners.
Data integrity requirements mandate that pharmaceutical tracking data be captured, stored, and maintained in formats that ensure accuracy and prevent tampering. Smart labeling systems incorporate advanced security measures including blockchain integration and cryptographic protection that provide immutable records of product handling and distribution.
Track and trace capabilities enable comprehensive product genealogy that documents the complete supply chain journey from manufacturing through patient delivery. These capabilities support regulatory investigations while enabling rapid response to quality issues or security concerns that may arise throughout the distribution process.
Advanced Analytics and Business Intelligence
Smart labeling systems generate vast amounts of supply chain data that provide unprecedented insights into pharmaceutical distribution performance, efficiency opportunities, and optimization strategies. Advanced analytics capabilities enable pharmaceutical companies to identify trends, predict demand patterns, and optimize distribution networks based on real-world performance data.
Predictive analytics applications utilize smart labeling data to anticipate supply chain disruptions, optimize inventory levels, and improve distribution efficiency through data-driven decision-making. These analytical capabilities support strategic planning while enabling proactive response to potential supply chain challenges.
Performance metrics derived from smart labeling systems enable comprehensive evaluation of supply chain partner performance, distribution route efficiency, and overall network effectiveness. These metrics support continuous improvement initiatives while providing objective data for partner evaluation and network optimization decisions.
Real-time visibility provided through smart labeling analytics enables dynamic response to changing market conditions, supply disruptions, or regulatory requirements. This responsiveness helps pharmaceutical companies maintain service levels while optimizing costs and ensuring compliance with evolving requirements.
Cost-Benefit Analysis and Economic Justification
The implementation of smart labeling systems requires significant investment in technology infrastructure, system integration, and operational modifications, but provides substantial return on investment through improved efficiency, reduced losses, and enhanced regulatory compliance capabilities.
Operational efficiency improvements through smart labeling typically include reduced manual handling, automated inventory management, and streamlined documentation processes that collectively reduce labor costs while improving accuracy and consistency. These efficiency gains often exceed implementation costs within the first year of operation.
Loss prevention benefits include reduced product theft, decreased counterfeiting risk, and improved inventory accuracy that collectively provide substantial cost savings. Smart labeling systems can reduce inventory discrepancies by up to 50 percent while enabling rapid identification and recovery of missing products.
Regulatory compliance benefits include reduced audit costs, streamlined inspection processes, and decreased risk of regulatory penalties that collectively provide significant value. The automated documentation capabilities of smart labeling systems often eliminate the need for extensive manual record-keeping while ensuring comprehensive compliance with regulatory requirements.
Future Innovations and Emerging Applications
The future of smart pharmaceutical labeling will be shaped by continued advances in wireless communication technologies, sensor capabilities, and data analytics that provide increasingly sophisticated tracking and monitoring capabilities. Fifth-generation wireless networks will enable enhanced communication capabilities while supporting more complex smart labeling applications.
Internet of Things integration will enable smart labels to communicate with broader sensor networks and environmental monitoring systems, creating comprehensive pharmaceutical tracking ecosystems that provide unprecedented visibility into product conditions and handling throughout the supply chain.
Artificial intelligence applications will enhance smart labeling systems through predictive analytics, automated decision-making, and adaptive optimization capabilities that continuously improve supply chain performance based on historical data and real-time conditions.
Blockchain integration will provide enhanced security and immutability for smart labeling data, creating tamper-proof records that support authentication and regulatory compliance while enabling secure data sharing among supply chain partners.
Implementation Strategies and Best Practices
Successful implementation of smart pharmaceutical labeling requires comprehensive planning that addresses technology selection, system integration, stakeholder training, and change management throughout organizations and supply chain networks. These implementation strategies must balance functionality requirements with cost considerations while ensuring compatibility with existing systems and processes.
Phased implementation approaches enable gradual deployment of smart labeling capabilities while minimizing disruption to existing operations. These approaches typically begin with high-value products or critical supply chain segments before expanding to comprehensive network coverage.
Stakeholder engagement involves collaboration with supply chain partners, regulatory authorities, and technology providers to ensure that smart labeling systems meet all requirements while providing maximum value to all participants. This engagement is essential for achieving interoperability and standardization across complex pharmaceutical supply networks.
Training and change management programs ensure that personnel throughout the supply chain understand and can effectively utilize smart labeling capabilities. These programs must address diverse user types and technical capabilities while ensuring consistent implementation of procedures and best practices.
Security and Data Protection Considerations
Smart labeling systems handle sensitive pharmaceutical supply chain data that requires comprehensive protection from cybersecurity threats, unauthorized access, and data manipulation. Security frameworks for smart labeling must address both physical label security and digital data protection throughout transmission and storage processes.
Encryption technologies protect data transmission between smart labels and reading systems while ensuring that sensitive information remains secure throughout the supply chain. These encryption approaches must balance security requirements with operational efficiency and compatibility across diverse systems and platforms.
Access control systems ensure that only authorized personnel can read or modify smart label data while maintaining audit trails that document all system interactions. These access controls must accommodate diverse user types and authorization levels while maintaining security and operational efficiency.
Data privacy considerations address patient information protection and commercial confidentiality requirements that govern pharmaceutical supply chain data. Smart labeling systems must comply with healthcare data protection regulations while supporting operational requirements and regulatory compliance obligations.
Conclusion: Transforming Pharmaceutical Supply Chain Excellence
Smart labeling technologies represent a fundamental transformation in pharmaceutical supply chain management, providing unprecedented visibility, security, and efficiency capabilities that support patient safety while optimizing operational performance. As these technologies continue to evolve and mature, pharmaceutical companies that embrace smart labeling solutions will achieve significant competitive advantages through improved supply chain control, enhanced regulatory compliance, and reduced operational costs.
The successful implementation of smart labeling requires ongoing commitment to technology innovation, stakeholder collaboration, and continuous improvement that adapts to changing regulatory requirements and market conditions. Through comprehensive smart labeling strategies, the pharmaceutical industry can achieve new levels of supply chain transparency and efficiency while maintaining the highest standards of product safety and patient care that define excellence in pharmaceutical operations.