The transformation of worldwide healthcare by way of digital innovation has reached a very critical inflection point in which the potential advantages of data-driven medicine should be carefully balanced against the fundamental ethical principles as well as privacy rights. It is well to be noted that healthcare data ecosystem ethics considerations have gone on to become central in shaping the sustainable, trustworthy, and inclusive digital healthcare infrastructure, which can serve a diverse set of populations while at the same time respecting the individual autonomy along with cultural values. This kind of evolving spectrum needs unmatched levels of international partnerships, standardization, and also governance frameworks that can adapt to the very fast-changing technological capacities.
The growing global healthcare data spectrum
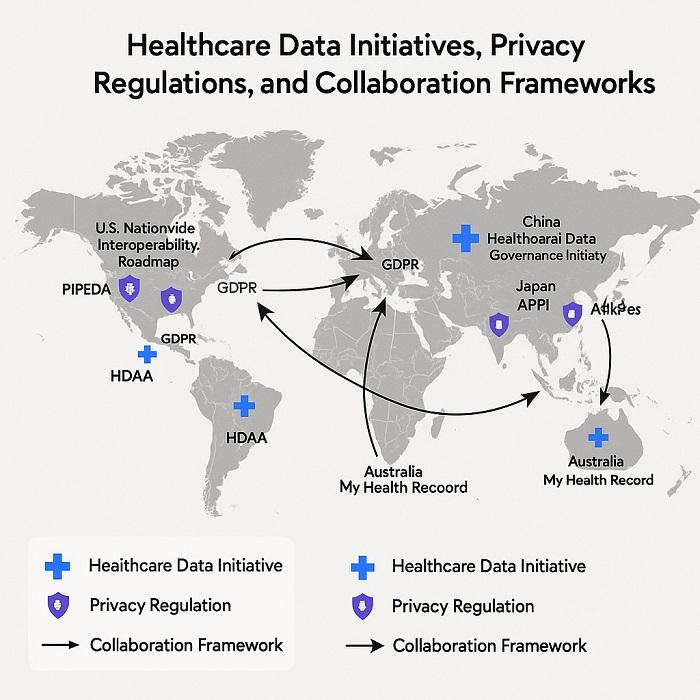 Global Healthcare Data Ecosystem Map showing initiatives and regulations worldwide
Global Healthcare Data Ecosystem Map showing initiatives and regulations worldwide
Healthcare data ecosystem ethics frameworks are getting redefined by the convergence of numerous technological, social, and regulatory forces, which are actually reshaping how health information gets collected, processed, and also used across borders. The European Health Data Space initiative blended with the similar endeavors in other regions goes on to demonstrate the rising recognition that puts forth the fact that healthcare data should be treated as both a valuable resource for advancing human health and also a protected asset that needs stringent safeguards.
The digital healthcare transformation initiative rolled out by the World Economic Forum goes on to exemplify the worldwide commitment to making utmost use of the public-private partnerships so as to improve the health outcomes while at the same time addressing the ethical concerns when it comes to data usage as well as sharing. These kinds of initiatives happen to recognize the massive majority of healthcare data, which at present remains unused in spite of its immense potential so as to enhance human health by way of creating opportunities along with responsibilities for stakeholders throughout the healthcare spectrum.
This transition towards treating healthcare data as being one of the global public goods represents a basic reimagining of data ownership along with stewardship models. This kind of an approach stresses collective advantages while at the same time maintaining the individual privacy along with consent rights that require sophisticated governance structures, which can actually balance the competing interests along with values throughout the diverse cultural as well as regulatory contexts.
Trust and transparency as foundational aspects
It is well to be noted that healthcare data ecosystem ethics principles stress that trust goes on to represent the basic prerequisite for any effective data sharing as well as utilization. Without public confidence in how health information is getting collected, stored, and even used,the most technologically sophisticated data systems will fail to achieve the expected advantages.
Building as well as maintaining this kind of trust needs unprecedented levels of transparency when it comes to data governance practices and also clear demonstration of tangible advantages to communities as well as individuals.
Interestingly, the reluctance of many entities to go ahead and share their health information crops up from the legitimate concerns when it comes to the misuse of data, violations in privacy, and also commercial exploitation of the information, which is sensitive and personal.
Taking into account such kinds of concerns needs comprehensive strategies, which include the data use policies that are transparent, very strong third-party verification systems, and a crystal-clear mechanism for individuals so that they understand and control how their individual data gets utilized.
Lessons pertaining to other sectors, especially finance, as well as telecommunications, offer certain valuable insights into successful approaches to overcome the initial resistance when it comes to data sharing while at the same time maintaining the right privacy protections. These examples go on to signify that the faith can be built by way of consistent demonstration when it comes to value, strict security practices, and stakeholder engagement within governance processes, which is very meaningful.
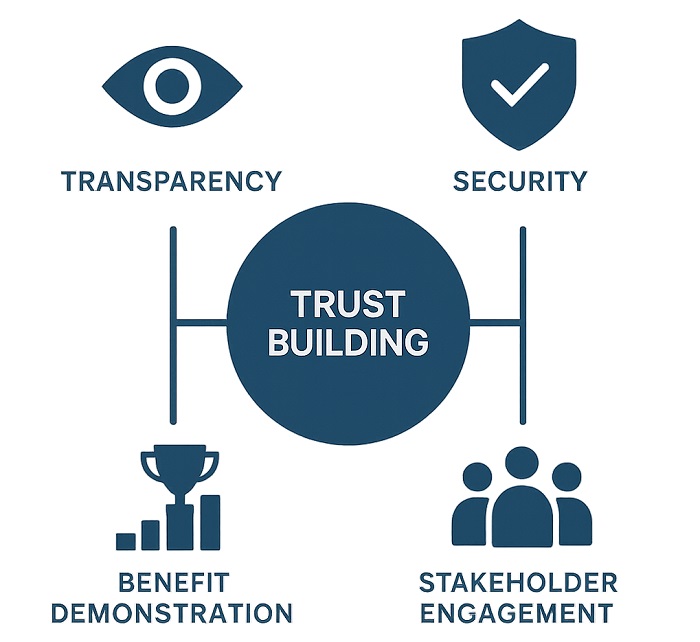 Trust Building Framework showing elements required for healthcare data trust
Trust Building Framework showing elements required for healthcare data trust
Interoperability along with standardization barriers
The dearth of interoperability within the healthcare data systems goes on to represent one of the most prominent barriers when it comes to realizing the complete potential of digital health transformation. Healthcare data ecosystem ethics considerations should address not just the technical interoperability barriers but also, at the same time, the fairness as well as equity implications when it comes to fragmented data systems, which may well perpetuate the present disparities found in healthcare.
The worldwide standards and their development efforts, which are inspired by successful frameworks such as the Helsinki Declaration for clinical trials, look forward to helping with seamless and secure data exchange throughout the international boundaries. But these standardization efforts should carefully balance the efficiency gains with regard to the local regulatory needs, cultural values, and also sovereignty concerns, which may vary quite significantly throughout different regions and also healthcare systems.
The development when it comes to the unified data standards needs extensive partnership between technical experts, healthcare providers, and regulators, as well as patient advocates, to make sure that interoperability solutions are technically robust and also acceptable socially. This kind of collaborative approach should address challenges with regard to data colonialism and also make sure that standardization efforts do not inadvertently disadvantage the less resourced healthcare systems or even populations.
Incentive alignment along with participation models
The healthcare data ecosystem ethics framework should address the basic challenge of aligning the incentives of the diverse stakeholders having different motivations and capacities and also constraints. Coming up with sustainable data-sharing ecosystems needs innovative approaches that encourage participation coming from industry, academia, healthcare providers, and also patients, and at the same time, making sure that advantages get distributed pretty fairly throughout the contributors.
Public-private partnerships, profit-sharing models, and community-driven development approaches go on to offer potential solutions when it comes to creating beneficial arrangements that are mutual and that encourage data contribution while at the same time respecting the contributor’s rights as well as interests. These kinds of models should be designed in order to safeguard exploitation of susceptible populations while at the same time encouraging a wide participation, which goes on to enhance the representativeness as well as utility of datasets that are shared.
The barrier of creating the right incentives is especially very intricate when it comes to global contexts in which the economic resources, regulatory framework, and also technological infrastructure vary dramatically. The solutions have to be flexible enough in order to accommodate these kinds of differences while at the same time maintaining the major ethical principles and also making sure that data-sharing advantages reach throughout all the participating communities.
Governance framework when it comes to ethical data usage
Strong governance frameworks go on to represent the cornerstone of ethical healthcare data ecosystems, offering the structures as well as processes that are necessary to ensure accountability, transparency, and also responsiveness to the concerns raised by stakeholders. Healthcare data Ecosystem ethics governance should address various levels of decision-making, right from individual consent management to global data sharing agreements.
The creation of codes of conduct, operation, and governance models along with third-party verification mechanisms needs a very careful equilibrium between flexibility and consistency, thereby helping that adaptation to local contexts while at the same time maintaining the universal ethical principles. These kinds of frameworks should be designed in order to evolve with the technologies, which are rapidly changing, and also social expectations while, at the same time, offering balanced foundations when it comes to commitments to long-term data stewardship.
Apparently, neutral platforms, which can facilitate multi-stakeholder governance and at the same time avoid the conflicts of interest, go on to represent a very promising approach in order to make sure that data ecosystem governance happens to serve a much wider public interest rather than a very narrow commercial or institutional aim. Such kinds of platforms should be designed with the right checks and balances in order to maintain the legitimacy as well as effectiveness throughout the stakeholder communities, which are diverse.
 Ethical Decision-Making Matrix for healthcare data use case evaluation
Ethical Decision-Making Matrix for healthcare data use case evaluation
Privacy protection along with individual rights
Healthcare data ecosystem ethics considerations should prioritize individual privacy rights while at the same time helping with beneficial usage of aggregated health information when it comes to research and public health purposes. Advanced privacy-preserving technologies, which include the likes of differential privacy, homomorphic encryption, and federated learning approaches, go on to offer a very promising solution for helping evaluation of sensitive health data without having the need for compromising on the privacy of the individual.
Apparently, the execution of privacy protection measures should go far beyond the technical solutions so as to include the comprehensive policy frameworks that go on to address consent management, purpose limitation, data minimization, and also control rights for individuals. These kinds of frameworks should be designed in order to look understandable and accessible to diverse populations while at the same time offering meaningful options when it comes to data usage along with sharing.
Global coordination when it comes to privacy standards along with individual rights protection is necessary for helping with cross-border data sharing while at the same time maintaining consistent protection levels. But this coordination should respect certain legitimate differences in terms of cultural values, legal traditions, and also regulatory approaches while at the same time establishing minimum benchmarks that safeguard the fundamental rights.
Automated decision-making along with artificial intelligence
The integration of artificial intelligence along with machine learning technologies within healthcare data ecosystems goes on to create opportunities as well as barriers. As far as ethical data usage is concerned. The healthcare data ecosystem ethics framework should address concerns with regard to algorithmic bias and accountability in automated decision-making systems and also transparency, which may prominently affect patient care along with health outcomes.
AI applications within healthcare data analysis can help with the detection of previously unrecognizable patterns along the relationships, which may as well lead to breakthrough insights in terms of disease prevention, diagnosis, and also treatment. But these similar capabilities often raise concerns when it comes to the potential for discriminatory outcomes, especially when one talks about underrepresented populations who may as well be inadequately represented in terms of training datasets.
Making sure that AI applications within healthcare data ecosystems go on to serve equitable as well as beneficial purposes needs ongoing tracking, assessment, and also alteration of algorithmic systems. This needs multidisciplinary expertise, blending technical knowledge along with understanding of healthcare delivery, community requirements, social justice principles, and also values.
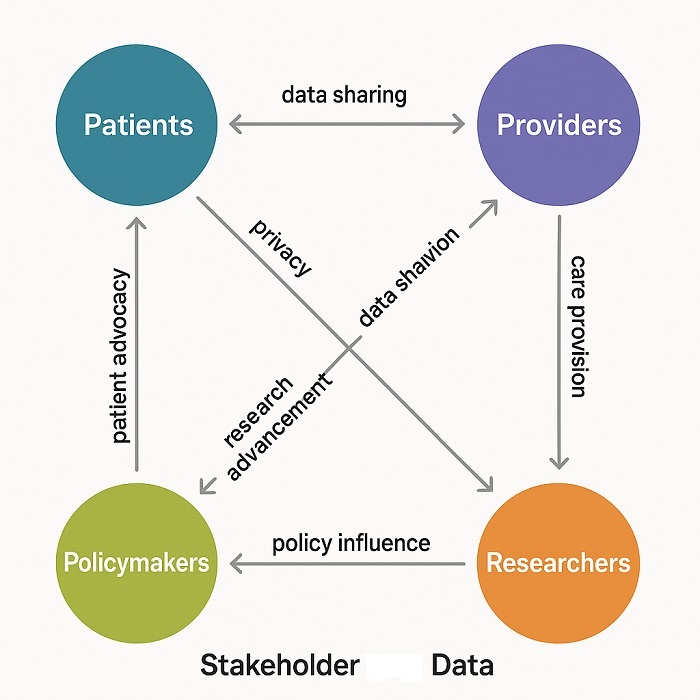 Stakeholder Ecosystem Diagram showing healthcare data stakeholder relationships
Stakeholder Ecosystem Diagram showing healthcare data stakeholder relationships
Global partnerships along with knowledge sharing
Healthcare data ecosystem ethics principles should facilitate worldwide collaboration while at the same time respecting the national sovereignty, varying levels in terms of technological development, and also cultural differences. International collaborations along with knowledge-sharing initiatives can speed up the progress towards common objectives while at the same time ensure that benefits as well as burdens are distributed equally and fairly between participating countries and communities.
The creation of global research networks along with collaborative platforms needs careful attention in order to power the dynamics, resource allocation, and also benefit distribution to make sure that national cooperation goes on to serve mutual interests and not just perpetuate the present inequalities. These kinds of partnerships should be designed so as to build local capacity along with expertise and not only create relationships that are dependent.
Global collaborations Pertaining to healthcare data, which is successful, it needs shared commitment when it comes to ethical principles, meaningful participation by all the stakeholders, and also transparent governance processes. This happens to include making sure that communities as well as countries that contribute data have the right representation in governance structures and also decision-making processes, which happen to affect their interest.
Long-term stewardship and sustainability
Healthcare data ecosystem ethics considerations should also address long-term sustainability in terms of data commitments by making sure that valuable health information is available for beneficial usage while being safeguarded from any kind of misuse or even exploitation. This needs sustainable funding models, great governance structures, and also institutional commitments that can adapt to the altering circumstances while, at the same time, maintaining the core principles of ethics.
The development when it comes to sustainable healthcare data ecosystems needs very careful attention to detail as well as economic models that can support the ongoing functions while at the same time avoid any kind of excessive commercialization, which may as well undermine the public trust or equitable access. These models should maintain the equilibrium between the need for financial stability and the commitment when it comes to serving the public interest objectives.
The long-term stewardship of healthcare data also needs attention to technological evolution by ensuring that data remain accessible and useful as technologies keep changing while at the same time maintaining security along with privacy protection. This needs the ongoing investments within data infrastructure, capabilities in terms of migration, and also preservation strategies that can actually adapt to the altering technical scenarios.
The healthcare data ecosystem ethics happen to represent a fundamental barrier and opportunity when it comes to transforming global health while at the same time respecting the individual rights and also community values.
The development of ethical, innovative, and collaborative healthcare data systems needs unmatched levels of coordination between the diverse stakeholders, commitment to transparency and accountability that is sustained, and ongoing adaptation to the altering technologies as well as social anticipations. The frameworks as well as the institutions that are developed today are going to shape the future of digital health for the years to come by paying careful attention to ethical principles along with inclusive governance, which is necessary so as to realize the transformative potential of healthcare data, while at the same time safeguarding the rights as well as interests of the people involved.