The biopharmaceutical sector is driven by rising global healthcare needs, technology, technological advancements, and the imperative to remain agile in a highly regulated environment. The need for increased efficiency, cost savings, and compressed timelines has resulted in the leading role played by CDMOs and advanced technologies.
The Role of CDMOs in Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing
The emergence of Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) has revolutionized the pharmaceutical landscape by providing pharmaceutical companies with rapid development and manufacturing assistance in a fast-moving industry. CDMOs offer services throughout the value chain and assist firms, including early development, clinical trials, and commercial manufacturing.
The manufacturing process complexity of biopharmaceuticals routinely contributes to increased production costs and longer timelines. The companies face huge pressure to innovate and bring treatments quickly while ensuring high-quality standards. To combat such adversity, the use of external expertise through CDMOs and advanced technologies in manufacturing is not a value addition anymoreŌĆöit is imperative.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Addressing Variable Production Requirements
The great value of working with a CDMO is that they can scale their manufacturing output for a variety of capacity needs. CDMOs provide additional advantages by managing a number of components of production simultaneously, such as formulation, analytics, and scale-up, so that the customer can complete projects in substantially shorter timelines.
For example, biopharmaceutical companies launching a monoclonal antibody treatment can trust CDMOs will efficiently scale their production as demand increases in the market. CDMOs have invested in cutting-edge modular systems that allow them to reorganize production lines and interface easily to allow a smooth transition in production lines, thereby saving time to market.
Furthermore, CDMOs are better equipped to handle the intricacies of the global supply chain. By diversifying manufacturing plants within designated geographical areas, CDMOs help mitigate the risk of disruptions at a local level and maintain business continuity.
- Cost Optimization: Reducing Capital Investments
The development and upkeep of cutting-edge manufacturing plants involve hefty capital expenditure, rendering it a prohibitive choice for most companies, particularly small and medium-sized biopharma companies. CDMOs enable organizations to sidestep these monetary limitations through the provision of access to top-notch facilities and know-how without bearing the cost of developing infrastructure internally.
Operational costs are also reduced with CDMOs because these companies bank on economies of scale. Bulk procurement of raw materials, shared use of facilities, and efficient logistics lead to appreciable cost savings. Companies can channel these savings into drug discovery, clinical development, and other core areas.
- Accelerating Time-to-Market: A Competitive Advantage
Speed is a determining element in the biopharmaceutical industry, with an impact on whether a firm can win market share in a crowded therapeutic space. CDMOs lead in shortening production timelines by virtue of their experience, pre-validated methods, and streamlined workflows.
For instance, in the case of the COVID-19 pandemic, CDMOs took center stage in speeding up vaccine development. By capitalizing on their already-established infrastructure and skilled personnel, they made it unnecessary for pharma companies to construct new buildings, making life-saving vaccines accessible to patients in an unprecedented time. Further, CDMOs’ capability to manage several areas of production simultaneously, including formulation, analytics, and scale-up, makes projects complete in less time.
- Regulatory Expertise: Overcoming Compliance Hurdles
Pharmaceuticals operate in a difficult position, navigating the intricate and detail-oriented regulatory environments of multiple international markets. CDMOs have extensive experience in complying with varied regulatory demands, including those from the FDA, EMA, and other foreign regulatory agencies. Their expertise in Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and quality standards helps ensure that products comply with all legal and safety standards.
CDMOs provide relevant experience, ensuring documentation, audit, and quality control in their working practices. CDMOs effectively free pharmacists to operate in the most innovative ways possible while providing confidence to pharmacists that the burdensome direction of the complexities of compliance is managed by a partner. This collaboration reduces the possibility of regulatory postponements and market entrance delays, hence increasing efficiency.
Advanced Technologies: The Engines of Transformation
Sophisticated technologies have become the foundation of modern biopharmaceutical production, addressing scalability, cost-effectiveness, quality, and sustainability concerns. Manufacturing operations are being transformed by technology that improves precision, consistency, and reduces the environmental footprint. Some of the most significant technologies that are shaping the industry’s future are discussed below.
- Single-Use Systems (SUS): Transforming Biopharma Facilities
Single-Use Systems (SUS) have quickly become a critical part of contemporary biopharmaceutical production. SUS comprises single-use bioreactors, mixers, and ultrafiltration systems, which swap disposable systems for traditional reusable equipment. The use of SUS brings numerous important benefits:
- The elimination of extended clean-in-place (CIP) and sterilize-in-place (SIP) procedures, which dramatically reduces downtime between runs.
- Improvement of operational flexibility by enabling quick flexibility for various production processes.
- Minimizing the risk of cross-contamination, a critical aspect in multiproduct facilities.
As an example, a biopharmaceutical company manufacturing a product pipeline can use single-use bioreactors to adjust manufacturing lines quickly for each product and do so without substantial cleaning validation burdens.
- Process Analytics and Real-Time Monitoring: Improving Quality Assurance
The deployment of Process Analytical Technology (PAT) has revolutionized biopharmaceutical manufacturing by allowing for live monitoring and control of critical process parameters during manufacturing while also not expending valuable human resources. PAT employs sophisticated sensors, spectroscopy, and data analytics to produce critical information that results in optimal product consistency and quality.
In upstream bioprocessing, PAT allows optimizing growth conditions for living cells, i.e., temperature, pH balance, and nutrient levels. Tracking these in real time allows manufacturers to reduce batch variability and increase yield.
- Digital Twins and Predictive Modeling: Connecting the Virtual and Physical Worlds
Digital twins, virtual models of physical production environments, are changing the way manufacturers optimize and make decisions. Through simulated manufacturing processes in a virtual setting, businesses can see where inefficiencies exist, experiment with possible process adjustments, and forecast results without interfering with actual manufacturing.
Predictive modelling is a related technology that applies historical data and machine learning techniques to provide predictive indications of upcoming barriers or outcomes. In conjunction, process digital twins and predictive modelling empower manufacturers to create process resilience, minimize risks, and optimize resource use.
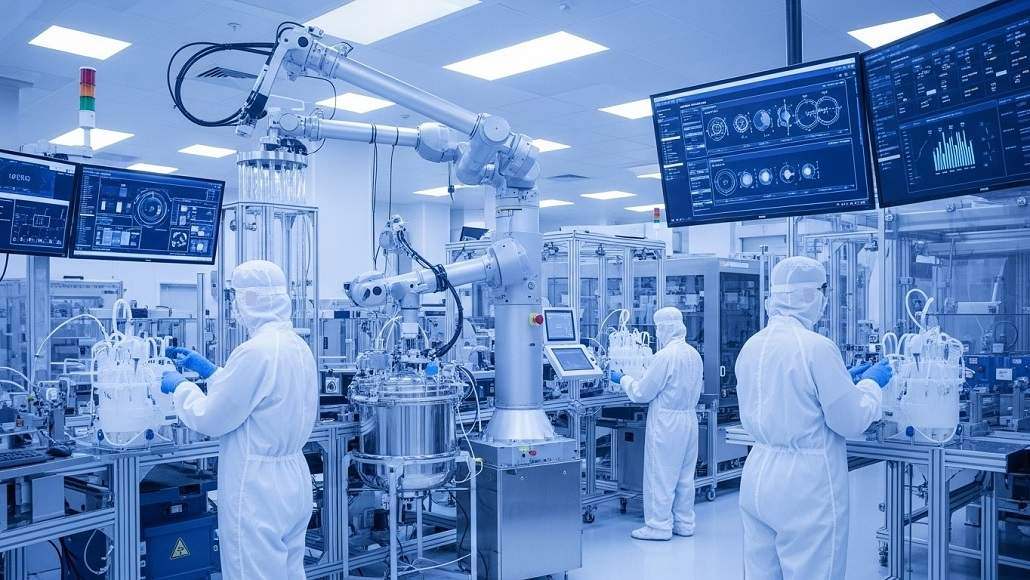
- Automation and Robotics: Precision in Every Step
Robotics and automation have transformed manufacturing processes, eliminating a significant amount of manual processes involved in operations and also enhancing precision. Automated processes are applied to every step of biopharmaceutical manufacturing, from aseptic filling and cell culture to packaging and labelling.
The latest developments in collaborative robots, or cobots, have further accelerated automation in manufacturing plants. Cobots interact with human operators, carrying out repetitive tasks while enabling skilled workers to concentrate on intricate problem-solving and decision-making.
- Continuous Manufacturing: A Paradigm Shift
Continuous production is a divergence from conventional batch processing and provides a wealth of efficiency and quality advantages. In contrast to batch production, in which manufacturing is broken into distinct phases, continuous production combines processes into a continuous flow. This allows for a constant stream of materials, less downtime, and greater efficiency. For example, continuous downstream processing methods, such as multicolumn chromatography, have transformed protein purification to allow for increased throughput and utilization of resources.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: Facilitating Smart Manufacturing
AI and machine learning (ML) are playing pivotal parts in making manufacturing smarter and more efficient. These technologies scan enormous datasets to identify patterns, streamline processes, and foretell potential problems before they occur.
Collaborative Synergy: CDMOs and Advanced Technologies
The incorporation of cutting-edge technologies in CDMO operations unlocks unprecedented efficiencies, forging a collaborative environment that propels biopharmaceutical manufacturing. The integration of CDMOs and advanced technologies has improved pharmaceutical businesses’ ability to produce faster production cycles, better resource utilization, and scalable solutions.
Conclusion
The combination of CDMOs and advanced technologies has revolutionised biopharmaceutical production, ushering in an era of efficiency, innovation, and flexibility. As the industry becomes more complicated, this marriage will play an increasingly important role in delivering faster, more inexpensive, and high-quality solutions.┬Ā Pharmaceutical companies, CDMOs, and technology suppliers must work together to fully realise this promise, which will eventually benefit patients worldwide by allowing for the prompt delivery of lifesaving therapies.