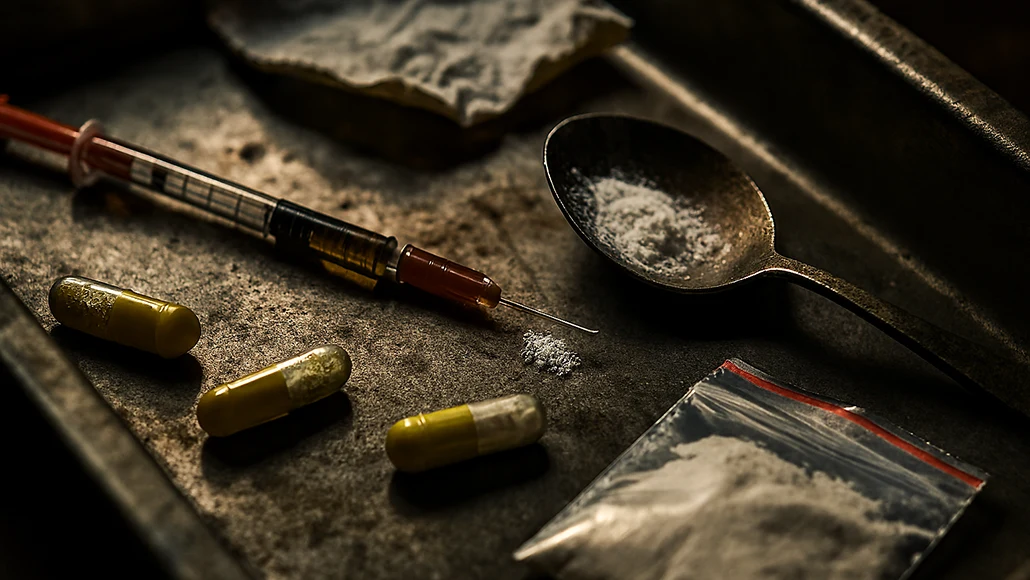
The landscape of drug usage has undergone significant changes in recent years, particularly with the rise of synthetic drugs. These substances, often engineered to mimic the effects of traditional illicit drugs, have raised alarm bells among health officials and law enforcement agencies. As we delve into the current state of synthetic drug usage, it is crucial to examine whether the situation is improving or deteriorating. While some aspects show signs of progress, the overall picture remains troubling.
The Rise of Synthetic Drugs
Synthetic drugs encompass a broad range of substances, including synthetic cannabinoids, synthetic cathinones (commonly known as “bath salts”), and various other designer drugs. These substances are often created in clandestine laboratories, allowing manufacturers to evade legal restrictions by slightly altering chemical structures. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), synthetic opioids, particularly fentanyl, have contributed to a dramatic increase in overdose deaths. In 2021, synthetic opioids were involved in over 70% of all opioid-related fatalities in the United States, highlighting the severity of the crisis.
The accessibility and potency of synthetic drugs have made them a growing concern. For instance, fentanyl is estimated to be 50 to 100 times more potent than morphine, making even a small dose potentially lethal. This potency, coupled with the fact that users may be unaware of the presence of fentanyl in other drugs, has led to a surge in accidental overdoses.
The Impact of Opiate Addiction
Opiates addiction remains a significant issue in the context of synthetic drug usage. The opioid crisis, which has been escalating for over two decades, has seen a shift from prescription painkillers to illicit drugs, including heroin and synthetic opioids. A report from the National Institute on Drug Abuse noted that nearly 80% of heroin users started with prescription opioids, illustrating the connection between legal drug use and subsequent addiction to more dangerous substances.
The impact of opiate addiction on individuals and communities is profound. Those struggling with addiction often face a myriad of challenges, including health complications, legal issues, and strained relationships. Additionally, the economic burden of the opioid crisis is staggering. The CDC estimates that the total economic burden of prescription opioid misuse alone in the United States is approximately £63 billion annually, factoring in healthcare costs, lost productivity, and criminal justice involvement.
Signs of Improvement
Despite the grim statistics surrounding synthetic drug usage and opiate addiction, there are signs of improvement in certain areas. Public awareness campaigns aimed at educating individuals about the dangers of synthetic drugs have gained traction. These initiatives seek to inform users about the risks associated with synthetic opioids and the potential for overdose. For example, the “Stop Overdose” campaign in the UK has been instrumental in raising awareness and providing resources for those affected by addiction.
Moreover, advancements in treatment options for opiate addiction are becoming more widely available. Medications such as buprenorphine and methadone can help manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings, providing individuals with a pathway to recovery. Additionally, the expansion of harm reduction strategies, such as needle exchange programmes and supervised consumption sites, has shown promise in reducing the negative consequences of drug use.
The Role of Legislation
Legislation plays a crucial role in addressing the synthetic drug crisis. Governments worldwide are beginning to implement stricter regulations on the production and distribution of synthetic drugs. For instance, the UK has introduced the Psychoactive Substances Act, which aims to prohibit the production and supply of new psychoactive substances. Such measures are essential in curbing the proliferation of synthetic drugs and protecting public health.
However, the challenge remains that manufacturers often adapt quickly to evade these regulations, creating new substances that fall outside legal definitions. This cat-and-mouse game complicates efforts to control synthetic drug usage and highlights the need for ongoing research and legislative adaptation.
Conclusion: A Complex Landscape
In conclusion, the state of synthetic drug usage presents a complex and multifaceted challenge. While there are signs of improvement in public awareness and treatment options for opiate addiction, the overall trend remains concerning. The potency and accessibility of synthetic drugs, particularly synthetic opioids like fentanyl, continue to pose significant risks to individuals and communities.
To effectively combat the growing synthetic drug crisis, a comprehensive approach is necessary. This includes enhancing education and prevention efforts, expanding access to treatment, and implementing robust legislative measures to regulate synthetic drug production. As society grapples with the realities of synthetic drug usage, it is imperative to remain vigilant and committed to finding solutions that prioritise health and wellbeing. The battle against opiate addiction and synthetic drug misuse is far from over, but with concerted effort, progress can be made in the fight for a safer future.