The Critical Challenge of Pharmaceutical Customs Clearance
The pharmaceutical industry faces unprecedented challenges in global supply chain management, particularly when navigating the complex landscape of international customs clearance for clinical trial materials and commercial drug batches. Customs delays can have devastating consequences, potentially compromising patient safety, disrupting clinical trial timelines, and resulting in millions of dollars in product losses due to temperature excursions or expiration dates .
The complexity of pharmaceutical customs clearance stems from the highly regulated nature of medicinal products, stringent documentation requirements, and the need for specialized handling of temperature-sensitive and controlled substances. Clinical trial shipments face additional challenges due to their investigational nature, requiring unique permits and regulatory approvals that differ from commercial pharmaceuticals .
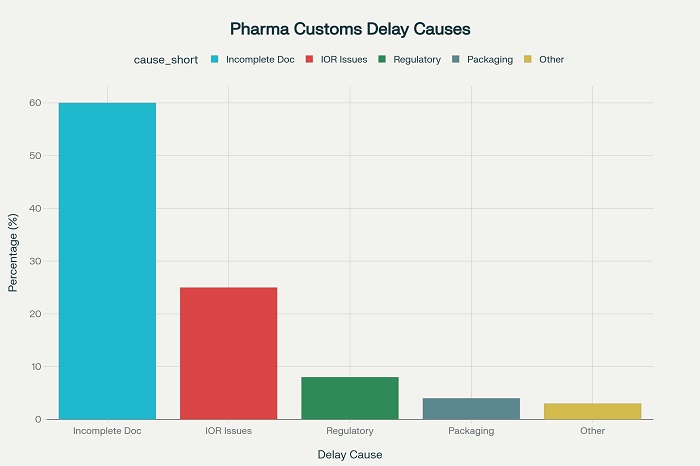
Recent industry analyses indicate that incomplete or incorrect documentation represents the leading cause of customs delays, accounting for approximately 60% of pharmaceutical shipment holds at international borders . The second most common issue involves problems with the Importer of Record (IOR) status, where the designated entity is not properly registered or recognized by the destination country’s customs authorities .
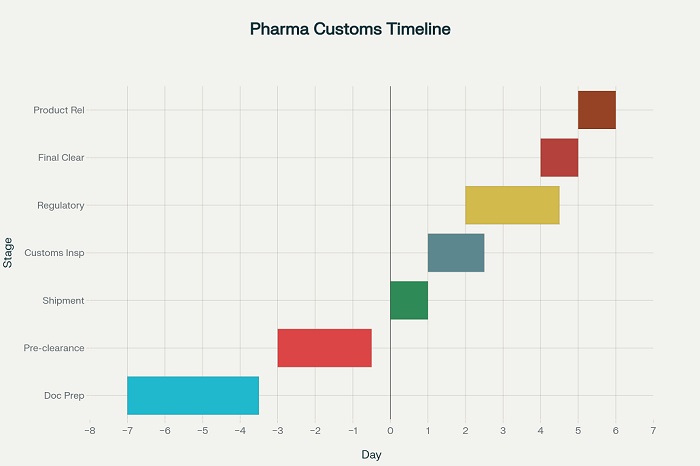
Understanding Regulatory Landscape and Documentation Requirements
Successful mitigation of customs delays begins with comprehensive understanding of the regulatory requirements in both origin and destination countries. Each jurisdiction maintains specific requirements for pharmaceutical imports, including licensing requirements, product registration status, and documentation standards that must be meticulously followed to ensure smooth clearance .
The harmonized system (HS) codes play a crucial role in customs classification, and pharmaceutical companies must ensure accurate product classification to prevent delays and incorrect duty assessments . Importantly, HS codes are not globally standardized, meaning the same product may have different classifications in different countries, requiring careful attention to local requirements.
Essential Documentation Framework
A comprehensive documentation package forms the foundation of successful customs clearance for pharmaceutical products. The core documents include detailed commercial invoices with accurate product descriptions, harmonized system codes, declared values reflecting true market value, and country of origin information . Each document must be prepared with meticulous attention to detail, as minor discrepancies can result in significant delays.
For clinical trial shipments, additional documentation requirements include clinical trial approvals, import licenses specific to investigational products, and statements clearly indicating the intended use and reason for import . Temperature-sensitive products require supplementary documentation demonstrating the maintenance of cold chain integrity throughout transit, including temperature monitoring records and handling instructions.
Regulatory Compliance Across Jurisdictions
Different regions maintain varying regulatory frameworks for pharmaceutical imports, requiring tailored approaches for each market. The European Union operates under Good Distribution Practice guidelines outlined in EudraLex Volume 4, while the United States follows FDA regulations under the Drug Supply Chain Security Act . Understanding these regional differences and preparing appropriate documentation for each jurisdiction is essential for avoiding delays.
The Falsified Medicines Directive in the EU mandates specific safety features and serialization requirements that must be documented during customs clearance . Similarly, other countries have implemented track-and-trace systems that require specific documentation and verification procedures during the import process.
Strategic Importer of Record Management
The selection and management of qualified Importers of Record represents a critical factor in preventing customs delays for pharmaceutical shipments. An IOR must be properly registered and recognized by the destination country’s customs authorities, with specific expertise in handling pharmaceutical products and understanding of local regulatory requirements .
Pharmaceutical companies must engage with IORs well in advance of shipping, ensuring proper registration and understanding of specific product requirements. The IOR should have demonstrated experience with similar products, particularly for controlled substances or investigational drugs that require specialized permits and handling procedures.
Proactive IOR Qualification Process
Effective IOR management requires a comprehensive qualification process that evaluates the entity’s regulatory standing, experience with pharmaceutical products, and capability to handle emergency situations. The qualification process should include verification of import licenses, assessment of local regulatory knowledge, and evaluation of communication protocols for addressing issues that may arise during clearance .
Companies should establish clear communication protocols with their IORs, ensuring that all necessary documentation is confirmed before shipment proceeds. This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of customs holds due to improper IOR status or missing documentation.
Technology Solutions and Digital Transformation
Modern customs clearance increasingly relies on digital solutions and automated documentation systems to streamline the process and reduce human error. Digital logistics platforms can automate documentation generation, integrate compliance checks, and provide real-time tracking of shipments through the customs process .
Automated documentation systems help ensure consistency and accuracy across all required documents, reducing the risk of discrepancies that commonly cause delays. These systems can incorporate up-to-date regulatory requirements and automatically flag potential issues before shipments are dispatched.
Real-Time Tracking and Communication Systems
Advanced tracking systems provide visibility throughout the customs clearance process, enabling proactive intervention when issues arise. These systems can integrate with customs databases to provide real-time updates on clearance status and automatically alert relevant stakeholders when delays occur .
Effective communication systems ensure that all parties involved in the clearance process, including freight forwarders, customs brokers, and regulatory authorities, have access to necessary information and can coordinate efficiently to resolve any issues that arise.
Risk Assessment and Contingency Planning
Comprehensive risk assessment methodologies enable pharmaceutical companies to identify potential customs clearance challenges and develop appropriate mitigation strategies. Risk factors include regulatory changes, geopolitical situations, seasonal variations in customs processing times, and specific challenges associated with controlled substances or investigational products .
Contingency planning should address various delay scenarios, including procedures for managing temperature-sensitive products during extended holds, alternative routing options, and expedited clearance procedures for critical shipments. These plans must be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changing conditions and regulatory requirements.
Seasonal and Geopolitical Considerations
Customs processing times can vary significantly based on seasonal factors, holiday periods, and geopolitical situations that may affect trade relationships. Companies must factor these considerations into their shipping schedules and contingency plans, allowing additional time during peak periods and maintaining awareness of political situations that may impact clearance procedures .
Geopolitical changes can result in new trade restrictions, modified documentation requirements, or changes in clearance procedures that must be quickly incorporated into shipping protocols. Maintaining awareness of these developments and adapting procedures accordingly is essential for avoiding unexpected delays.
Specialized Handling for Clinical Trial Materials
Clinical trial shipments present unique challenges due to their investigational nature and the critical timing requirements for study protocols. These shipments often require specialized import permits that may be issued on a one-time or periodic basis, requiring careful coordination with regulatory authorities .
The complexity of clinical trial customs clearance is further increased when dealing with controlled substances, compassionate use therapies, or products requiring ultra-cold chain management. These shipments may require additional regulatory approvals and specialized handling procedures that must be coordinated well in advance of shipping.
Investigational Product Documentation
Clinical trial materials require specific documentation that clearly identifies their investigational status and intended use. This documentation must align with clinical trial approvals and regulatory permissions in the destination country, requiring close coordination between clinical operations and logistics teams .
The documentation package should include detailed product information, clinical trial protocol references, and clear statements regarding the investigational nature of the products. Any controlled substances require additional permits and documentation demonstrating compliance with narcotics regulations.
Commercial Drug Batch Considerations
Commercial pharmaceutical shipments face different but equally complex requirements, including product registration verification, batch documentation, and compliance with Good Distribution Practice standards. Commercial shipments may be subject to random inspections and quality verifications that can extend clearance times .
Batch-specific documentation must demonstrate compliance with manufacturing standards, quality control testing, and stability requirements. This documentation becomes particularly important for temperature-sensitive products where customs authorities may require evidence of maintained cold chain integrity.
Serialization and Track-and-Trace Compliance
Many countries have implemented serialization requirements for pharmaceutical products, requiring specific documentation and verification procedures during customs clearance. These systems help prevent counterfeit products from entering the supply chain but add complexity to the clearance process .
Companies must ensure that their serialization data is properly formatted and accessible to customs authorities, with appropriate documentation demonstrating compliance with local track-and-trace requirements.
Best Practices for Delay Prevention
Successful mitigation of customs delays requires implementation of comprehensive best practices that address all aspects of the clearance process. These practices include thorough documentation preparation, proactive communication with all stakeholders, and regular review of procedures to incorporate lessons learned and regulatory changes .
Companies should establish clear standard operating procedures for customs clearance, with specific protocols for different product types, destinations, and shipment categories. Regular training of personnel involved in the clearance process ensures consistent execution of these procedures and reduces the risk of errors that could cause delays.
Continuous Improvement and Learning
Effective delay mitigation requires continuous analysis of clearance performance and identification of improvement opportunities. Companies should maintain detailed records of clearance times, delay causes, and resolution methods to identify patterns and develop targeted improvement strategies .
Regular review meetings with customs brokers, freight forwarders, and IORs can provide valuable insights into changing requirements and opportunities for process improvement. This collaborative approach helps ensure that all parties are aligned on procedures and requirements.
The successful mitigation of customs delays for clinical trial shipments and commercial drug batches requires a comprehensive approach that addresses documentation requirements, regulatory compliance, technology solutions, and stakeholder management. Companies that invest in robust customs clearance processes and maintain proactive relationships with all stakeholders will be better positioned to ensure timely delivery of critical pharmaceutical products while maintaining compliance with all regulatory requirements. The complexity of global pharmaceutical logistics continues to increase, making these capabilities essential for success in the international marketplace.