Patient-Centric Packaging Solutions for Improved Compliance
The pharmaceutical industry has undergone a fundamental transformation in its approach to medication packaging, with patient-centric pharma packaging emerging as a critical driver of therapeutic success and improved health outcomes. This evolution represents a shift from packaging that merely protects medications to comprehensive systems that actively support patient adherence, enhance safety, and improve the overall medication experience for diverse patient populations.
Understanding Patient-Centric Design Philosophy
Patient-centric packaging represents the integration of pharmaceutical product packaging with patients’ needs for accessibility, information, and instruction in medication use. This approach recognizes that packaging serves as a crucial interface between patients and their treatments, directly influencing adherence rates, safety outcomes, and therapeutic effectiveness. The philosophy encompasses three interconnected elements: patient adherence, patient outcomes, and patient experience, creating a comprehensive framework for packaging innovation.
The global medication adherence packaging market has experienced significant growth as healthcare stakeholders recognize the critical role packaging plays in therapeutic success. Research indicates that improving medication adherence through packaging interventions can have a greater impact on population health than advances in specific medical treatments, highlighting the transformative potential of thoughtful packaging design.
Traditional pharmaceutical packaging focused primarily on product protection and regulatory compliance, often overlooking the human factors that influence medication use. Contemporary patient-centric approaches integrate ergonomic design, clear communication, and accessibility features that address the diverse needs of patient populations, from pediatric to geriatric users and those with various physical or cognitive limitations.
Addressing Age-Related Challenges Through Inclusive Design
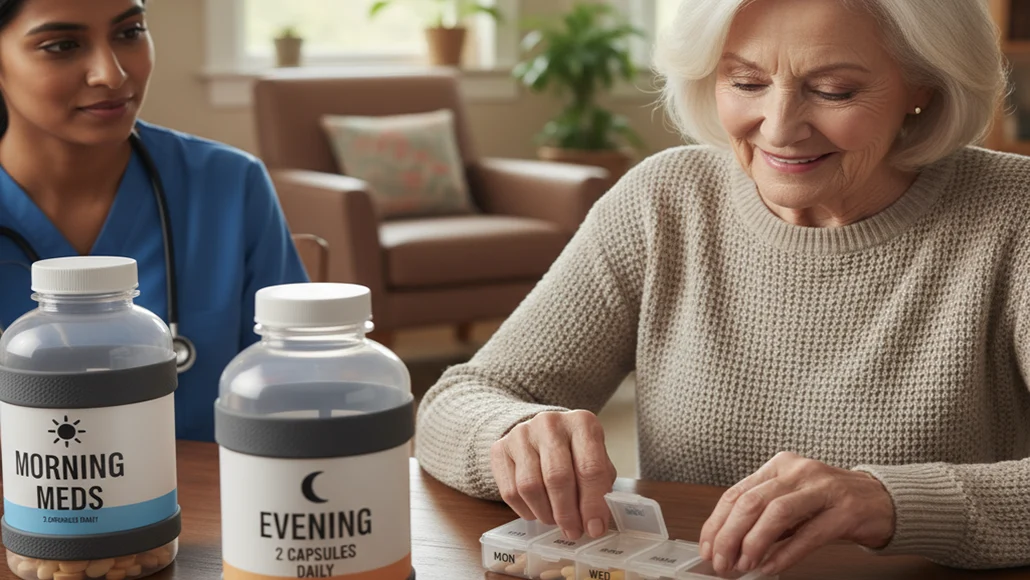
The aging global population presents unique challenges for pharmaceutical packaging design, as elderly patients often experience reduced dexterity, grip strength, and visual acuity that can impede medication access. Patient-centric packaging solutions address these challenges through ergonomic improvements, enhanced visibility features, and simplified opening mechanisms that maintain safety while improving accessibility.
Senior-friendly packaging design principles focus on reducing the physical effort required to access medications while preserving child-resistant properties where necessary. These designs typically incorporate larger gripping surfaces, improved visual contrast, and opening mechanisms that require less force or complex manipulation, enabling elderly patients to maintain independence in medication management.
Research demonstrates that well-designed packaging can significantly improve medication adherence among elderly populations. Studies show that packaging modifications such as easy-open blister packs, high-contrast labeling, and clear instructions can increase adherence rates by up to 25 percent among seniors, directly impacting health outcomes and reducing healthcare costs associated with non-adherence.
The development of push-pack technologies represents a significant advancement in senior-friendly packaging, offering single-dose accessibility that reduces confusion while maintaining child-resistant properties. These innovations demonstrate how thoughtful design can address multiple patient needs simultaneously, providing safety, convenience, and clarity in a single packaging solution.
Technology Integration for Enhanced Patient Engagement
Modern patient-centric packaging increasingly incorporates digital technologies that extend beyond physical accessibility to provide interactive features that support medication management and patient education. Smart packaging solutions integrate near-field communication chips, QR codes, and sensors that connect patients with digital resources and monitoring capabilities through their smartphones.
Digital adherence monitoring through smart packaging enables real-time tracking of medication-taking behavior, providing valuable insights for both patients and healthcare providers. These systems can detect when medications are removed from packaging and provide reminders, education, or alerts about missed doses, creating a comprehensive support system for medication management.
Interactive educational content delivered through smart packaging enables patients to access instructional videos, dosage information, and safety warnings by simply tapping their smartphones on medication containers. This technology transforms packaging from a passive container into an active educational tool that can improve understanding and adherence while reducing medication errors.
Temperature monitoring capabilities integrated into smart packaging provide additional safety assurance for temperature-sensitive medications, alerting patients when products may have been exposed to conditions that could affect efficacy. This functionality is particularly valuable for biologics and other sensitive therapies that require careful environmental control.
Medication Adherence Solutions and Behavioral Support
Packaging interventions specifically designed to improve medication adherence have demonstrated significant effectiveness across diverse patient populations and therapeutic areas. Multi-dose packaging systems organize medications by time and date, reducing confusion and making complex medication regimens more manageable for patients with multiple prescriptions.
Blister packaging with calendar formats provides visual cues that help patients track their medication-taking behavior while identifying missed doses quickly and easily. These systems are particularly effective for patients managing chronic conditions that require consistent daily medication, providing both organizational support and adherence feedback.
Strip packaging innovations enable unit-dose dispensing that reduces medication errors while providing clear identification of each dose. These systems can incorporate multiple medications for specific administration times, simplifying complex regimens while maintaining accurate dosing and reducing the risk of therapeutic errors.
Automated dispensing systems integrated with packaging solutions provide timed medication release that supports adherence while reducing the burden of medication management on patients and caregivers. These systems can be programmed to accommodate complex dosing schedules while providing feedback and monitoring capabilities that support clinical oversight.
Addressing Specific Patient Population Needs
Pediatric pharmaceutical packaging requires specialized design considerations that balance safety, accessibility, and engagement appropriate for different developmental stages. Child-friendly packaging must maintain safety features while incorporating age-appropriate design elements that facilitate proper use and reduce resistance to medication-taking.
Visual design elements in pediatric packaging can reduce anxiety and fear associated with medication while providing clear instructions appropriate for different reading levels and cognitive development stages. These design approaches recognize that packaging appearance and functionality can significantly influence medication acceptance and adherence among young patients.
Caregiver-focused packaging features address the reality that many medications are administered by family members or healthcare providers rather than patients themselves. These design elements include clear labeling, easy identification systems, and safety features that support accurate administration while reducing the risk of errors.
Accessibility features for patients with disabilities encompass a broad range of design modifications including tactile indicators for visually impaired patients, easy-grip surfaces for those with limited hand function, and clear audio instructions for patients with various cognitive or sensory limitations.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Integration
Patient-centric packaging must navigate complex regulatory requirements while maintaining safety standards and incorporating user-friendly features. Regulatory frameworks such as FDA guidelines and international standards provide frameworks for evaluating packaging accessibility without compromising safety or product integrity.
Child-resistant packaging requirements must be balanced with accessibility needs for adult patients, creating design challenges that require innovative solutions. Contemporary approaches utilize testing protocols that evaluate both child resistance and adult accessibility, ensuring that safety features do not inadvertently create barriers for intended users.
Tamper-evident features integrated into patient-centric packaging provide security and authentication while maintaining ease of use for legitimate patients. These features must be obvious enough to detect tampering while not creating unnecessary complexity in normal use situations.
Labeling requirements for patient-centric packaging encompass both regulatory mandates and user experience considerations, requiring clear presentation of essential information in formats that support understanding and appropriate use across diverse patient populations.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Considerations
The production of patient-centric pharmaceutical packaging requires specialized manufacturing capabilities that can accommodate complex design features while maintaining the precision and quality standards essential to pharmaceutical applications. Advanced manufacturing techniques enable the integration of multiple functional elements into single packaging systems that address diverse patient needs.
Quality control processes for patient-centric packaging must evaluate both functional performance and user experience characteristics, ensuring that accessibility features work consistently while maintaining product protection and safety capabilities. These quality systems require comprehensive testing protocols that simulate real-world use conditions across diverse patient populations.
Supply chain management for patient-centric packaging involves coordination between pharmaceutical manufacturers, packaging suppliers, and healthcare providers to ensure that specialized packaging reaches appropriate patient populations. This coordination is particularly important for customized packaging solutions that address specific therapeutic areas or patient demographics.
Cost management strategies for patient-centric packaging focus on achieving cost-effectiveness through design optimization, manufacturing efficiency, and demonstrated value in improved patient outcomes. While initial costs may exceed standard packaging, the total healthcare value including improved adherence and reduced complications often provides compelling economic justification.
Measuring Outcomes and Continuous Improvement
Evaluation of patient-centric packaging effectiveness requires comprehensive metrics that assess both clinical outcomes and patient experience indicators. Adherence measurement through packaging monitoring provides objective data about medication-taking behavior while patient feedback surveys capture subjective experience factors that influence long-term compliance.
Clinical outcome assessment examines the relationship between packaging design and therapeutic effectiveness, measuring parameters such as disease control, hospitalization rates, and quality of life indicators that may be influenced by improved medication adherence and reduced medication errors.
Patient satisfaction metrics evaluate the user experience aspects of packaging design, including ease of use, clarity of instructions, and overall satisfaction with the medication management experience. These metrics provide valuable feedback for continuous improvement in packaging design and functionality.
Healthcare economic analysis examines the cost-effectiveness of patient-centric packaging interventions, measuring factors such as reduced healthcare utilization, improved therapeutic outcomes, and reduced medication waste that result from improved adherence and appropriate use.
Future Innovations and Emerging Trends
The future of patient-centric pharmaceutical packaging will be shaped by continued advances in digital health technology, personalized medicine approaches, and deeper understanding of human factors that influence medication behavior. Artificial intelligence integration will enable packaging systems that learn from patient behavior and adapt to provide increasingly personalized support and intervention.
Personalized packaging solutions will utilize patient data and preferences to create customized packaging experiences that address individual needs, preferences, and challenges. These approaches may incorporate variable design elements, personalized instructions, or adaptive features that respond to changing patient capabilities over time.
Integration with healthcare delivery systems will enable packaging that communicates directly with electronic health records, pharmacy management systems, and clinical decision support tools, creating comprehensive medication management ecosystems that support both patients and healthcare providers.
Sustainability considerations will drive the development of patient-centric packaging solutions that balance user experience with environmental responsibility, incorporating biodegradable materials and circular economy principles while maintaining functionality and safety standards.
Conclusion: Transforming Healthcare Through Thoughtful Design
Patient-centric packaging solutions represent a fundamental evolution in pharmaceutical care delivery, transforming medication packaging from passive containers into active partners in therapeutic success. As the healthcare industry continues to recognize the critical role that packaging plays in patient outcomes, investment in patient-centric design will become increasingly important for pharmaceutical companies seeking to maximize the therapeutic value of their products.
The successful implementation of patient-centric packaging requires collaboration across multiple disciplines including packaging engineering, human factors psychology, clinical research, and regulatory affairs. Through this interdisciplinary approach, the pharmaceutical industry can create packaging solutions that truly serve patients while supporting broader healthcare objectives of improved outcomes, reduced costs, and enhanced quality of life for individuals managing various health conditions.