Building Robust Supply Chain Networks Through Strategic Packaging Design
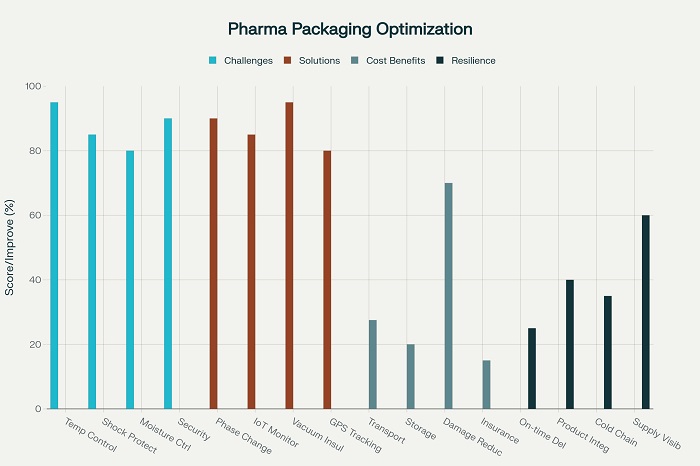
The pharmaceutical industry faces unprecedented challenges in maintaining supply chain resilience while ensuring product integrity throughout increasingly complex global distribution networks. Optimizing pharma packaging for shipping and distribution has become a critical strategic imperative that extends far beyond protective functionality to encompass supply chain risk mitigation, sustainability objectives, and operational efficiency enhancement. Modern pharmaceutical companies must develop comprehensive packaging strategies that address multiple distribution scenarios while maintaining the stringent quality and safety standards essential to pharmaceutical applications.
The evolution of global pharmaceutical distribution networks has created new demands for packaging solutions that can withstand diverse transportation modes, climate conditions, and handling environments while preserving product efficacy and regulatory compliance. These challenges have driven innovation in protective packaging materials, temperature control technologies, and smart monitoring systems that provide real-time visibility into product condition throughout the distribution journey.
Contemporary pharmaceutical supply chains have become increasingly complex, with products often traveling through multiple distribution centers, transportation modes, and international borders before reaching their final destinations. This complexity demands packaging solutions that maintain product integrity across varied environmental conditions while supporting efficient handling, storage, and tracking throughout the distribution network. The COVID-19 pandemic further highlighted the critical importance of supply chain resilience, demonstrating how distribution disruptions can directly impact patient access to essential medications.
Advanced Protective Packaging Technologies
The development of advanced protective packaging materials has revolutionized pharmaceutical distribution by providing superior protection against environmental hazards while enabling weight reduction and sustainability improvements. These materials utilize innovative polymer structures, advanced barrier technologies, and smart design approaches that optimize protection while minimizing material consumption and transportation costs.
Multi-layer barrier films have emerged as essential components of pharmaceutical distribution packaging, providing comprehensive protection against moisture, oxygen, and temperature fluctuations that could affect product stability. These films utilize sophisticated coextrusion processes that create ultra-thin barrier layers with exceptional performance characteristics. Advanced barrier technologies can achieve moisture vapor transmission rates below 0.01 g/m²/day while maintaining flexibility and durability required for distribution applications.
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) packaging has proven particularly effective for pharmaceutical distribution applications requiring temperature control and impact protection. EPS materials provide exceptional insulation properties that maintain product temperature while offering superior cushioning against mechanical shocks during transportation. The lightweight characteristics of EPS materials reduce shipping costs while providing reliable protection for temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical products.
Insulated shipping containers utilizing phase change materials (PCMs) have revolutionized cold chain distribution for temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals. These containers maintain specific temperature ranges for extended periods without external power sources while providing comprehensive protection against temperature excursions. PCM-based containers can maintain temperatures within ±2°C for up to 120 hours, enabling long-distance distribution of vaccines, biologics, and other temperature-sensitive medications.
Temperature Control and Cold Chain Management
Temperature control represents one of the most critical aspects of pharmaceutical distribution packaging, particularly for biologics, vaccines, and other temperature-sensitive products that require maintained cold chain integrity throughout the distribution process. Advanced temperature control packaging systems utilize sophisticated insulation materials, monitoring technologies, and backup systems that ensure temperature maintenance even during distribution disruptions.
Passive temperature control systems have become increasingly sophisticated, utilizing advanced insulation materials and thermal mass management to maintain required temperatures without external power sources. These systems incorporate vacuum insulation panels, reflective barriers, and optimized airflow designs that maximize thermal performance while minimizing package size and weight. Modern passive systems can maintain 2-8°C temperatures for up to seven days while providing reliable protection against temperature excursions.
Active temperature control systems provide precise temperature management through integrated cooling and heating systems that respond to external temperature variations. These systems utilize thermoelectric cooling, mechanical refrigeration, or hybrid approaches that maintain precise temperature control throughout extended distribution periods. Active systems provide superior temperature control but require more complex packaging designs and higher costs compared to passive alternatives.
Temperature monitoring and data logging systems have become essential components of pharmaceutical cold chain packaging, providing real-time visibility into product temperature throughout the distribution journey. These systems utilize wireless sensors, GPS tracking, and cloud-based monitoring platforms that enable continuous temperature monitoring while providing alerts when temperature excursions occur. Advanced monitoring systems can predict potential temperature problems and recommend corrective actions before product integrity is compromised.
Shock and Vibration Protection Strategies
Pharmaceutical products require comprehensive protection against mechanical shocks and vibrations that occur during transportation and handling throughout the distribution network. These mechanical stresses can affect product integrity, packaging seal quality, and overall product stability, making effective shock and vibration protection essential for pharmaceutical distribution packaging.
Cushioning systems designed specifically for pharmaceutical applications utilize advanced materials and engineering approaches that provide optimal protection while minimizing package size and weight. Molded pulp cushioning provides excellent shock absorption characteristics while offering environmental benefits through recyclable construction. Foam cushioning systems utilize engineered densities and cell structures that provide optimal protection for specific pharmaceutical products while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Suspension packaging systems isolate pharmaceutical products from external vibrations and shocks through mechanical isolation techniques that prevent transmission of mechanical energy to the product. These systems utilize spring mechanisms, elastic materials, or pneumatic isolation that effectively decouple products from transportation-induced vibrations. Suspension systems prove particularly effective for fragile pharmaceutical products such as glass vials and ampoules that are susceptible to mechanical damage.
Vibration analysis and testing protocols have become essential components of pharmaceutical packaging development, ensuring that packaging systems provide adequate protection against the mechanical stresses encountered during distribution. These testing programs utilize standardized vibration profiles that simulate transportation conditions while evaluating packaging performance under controlled laboratory conditions. Testing results guide packaging design optimization and validate protection capabilities for specific distribution scenarios.
Smart Packaging and Real-Time Monitoring
The integration of smart technologies into pharmaceutical distribution packaging has created unprecedented visibility and control capabilities that enhance supply chain management while ensuring product integrity throughout the distribution process. These technologies utilize sensors, communication systems, and data analytics platforms that provide real-time information about product condition, location, and handling throughout the supply chain.
Internet of Things (IoT) sensors embedded in pharmaceutical packaging provide continuous monitoring of environmental conditions, handling activities, and package integrity throughout the distribution journey. These sensors track temperature, humidity, shock levels, and light exposure while transmitting data to cloud-based monitoring platforms that enable real-time visibility and alerting. IoT integration creates comprehensive audit trails that support quality assurance and regulatory compliance requirements.
GPS tracking systems integrated with pharmaceutical packaging enable precise location monitoring and route optimization that enhances supply chain efficiency while providing security against theft and diversion. These systems provide real-time location information while supporting automated inventory management and delivery confirmation. GPS integration enables optimized routing that reduces transportation time and costs while improving delivery reliability.
Blockchain integration with smart packaging creates immutable records of distribution activities that support traceability, authentication, and supply chain transparency. These distributed ledger systems provide tamper-proof documentation of product handling, environmental conditions, and chain of custody throughout the distribution network. Blockchain technology enhances security while supporting regulatory compliance and investigation activities.
Sustainability Integration and Environmental Considerations
Environmental sustainability has become an increasingly important consideration in pharmaceutical distribution packaging design, driving innovation in materials selection, design optimization, and end-of-life management strategies. These sustainability initiatives must balance environmental objectives with essential protection requirements while maintaining cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency.
Renewable material integration in pharmaceutical distribution packaging utilizes plant-based polymers, recycled content materials, and biodegradable alternatives that reduce environmental impact while maintaining essential protective characteristics. Bio-based insulation materials derived from agricultural waste provide effective temperature control while offering superior environmental profiles compared to traditional synthetic alternatives.
Packaging optimization strategies focus on material reduction, design efficiency, and multi-use capabilities that minimize environmental impact while maintaining protection performance. Right-sizing initiatives ensure that packaging dimensions match product requirements while eliminating unnecessary material consumption. Modular packaging systems enable component reuse and recycling while supporting various product configurations and distribution scenarios.
Circular economy principles have been integrated into pharmaceutical distribution packaging through design for recyclability, reusable component systems, and closed-loop material recovery programs. These initiatives create sustainable packaging ecosystems that minimize waste generation while supporting cost reduction and environmental objectives. Successful circular economy implementations demonstrate that sustainability and performance objectives can be achieved simultaneously through intelligent design and material selection.
Regulatory Compliance and Quality Assurance
Pharmaceutical distribution packaging must comply with comprehensive regulatory requirements that ensure product safety, efficacy, and quality throughout the distribution process. These requirements encompass material compatibility, stability testing, and documentation standards that demonstrate packaging system reliability and regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions.
Good Distribution Practice (GDP) regulations establish comprehensive requirements for pharmaceutical distribution packaging that ensure product integrity throughout the supply chain. These regulations address packaging material selection, handling procedures, and environmental controls that maintain product quality during distribution. GDP compliance requires comprehensive documentation and monitoring systems that demonstrate adherence to established standards.
Stability testing programs for pharmaceutical distribution packaging validate packaging performance under accelerated aging conditions that simulate extended distribution and storage scenarios. These testing programs evaluate material stability, barrier property retention, and protective performance over time while supporting regulatory submissions and shelf-life determinations. Stability testing results provide confidence in packaging performance throughout the product lifecycle.
International shipping regulations present additional complexity for pharmaceutical distribution packaging, requiring compliance with dangerous goods regulations, customs requirements, and country-specific import standards. These regulations often require specialized packaging designs, documentation procedures, and handling protocols that ensure safe transportation while maintaining regulatory compliance across international borders.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Effective risk management strategies for pharmaceutical distribution packaging address potential supply chain disruptions, quality issues, and security threats that could affect product integrity or delivery reliability. These strategies encompass risk assessment, mitigation planning, and contingency procedures that maintain supply chain resilience under adverse conditions.
Supply chain risk assessment identifies potential vulnerabilities in distribution networks, packaging systems, and operational procedures that could affect product delivery or integrity. These assessments consider natural disasters, transportation disruptions, security threats, and quality issues while evaluating their potential impact on pharmaceutical distribution operations. Risk assessment results guide mitigation strategy development and contingency planning activities.
Diversification strategies reduce supply chain risk through multiple packaging suppliers, alternative distribution routes, and redundant inventory positioning that provides flexibility during disruptions. These strategies ensure that pharmaceutical products can continue to reach patients even when primary distribution channels are compromised. Diversification requires careful coordination and additional costs but provides essential resilience against supply chain disruptions.
Emergency response procedures address potential distribution emergencies through predefined protocols that ensure rapid response and product protection during crisis situations. These procedures encompass natural disasters, transportation accidents, security incidents, and quality issues while providing clear guidance for preserving product integrity and maintaining patient access to essential medications.
Technology Integration and Digital Solutions
Digital technologies have become integral components of pharmaceutical distribution packaging systems, enabling enhanced monitoring, optimization, and management capabilities that improve supply chain performance while reducing operational costs. These technologies encompass data analytics, artificial intelligence, and automation systems that create comprehensive distribution management platforms.
Predictive analytics applications utilize historical distribution data, environmental conditions, and packaging performance information to predict potential issues and optimize distribution strategies. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and trends that inform packaging design decisions, route optimization, and risk mitigation strategies. Predictive capabilities enable proactive management that prevents problems rather than responding to issues after they occur.
Automated packaging systems optimize pharmaceutical distribution through robotic handling, intelligent sorting, and automated quality control that enhance efficiency while reducing human error. These systems integrate with warehouse management platforms and transportation management systems to create seamless distribution operations that minimize handling time and reduce damage risk.
Digital twin technology creates virtual models of distribution packaging systems that enable comprehensive testing, optimization, and monitoring without physical prototyping. These virtual systems support packaging design optimization, performance prediction, and troubleshooting activities while reducing development time and costs. Digital twin applications become increasingly sophisticated as they incorporate real-world performance data and machine learning capabilities.
Economic Optimization and Cost Management
Cost optimization in pharmaceutical distribution packaging requires balanced consideration of protection requirements, material costs, transportation expenses, and operational efficiency while maintaining quality and regulatory compliance. Effective cost management strategies identify optimization opportunities that reduce total distribution costs while enhancing packaging performance and sustainability.
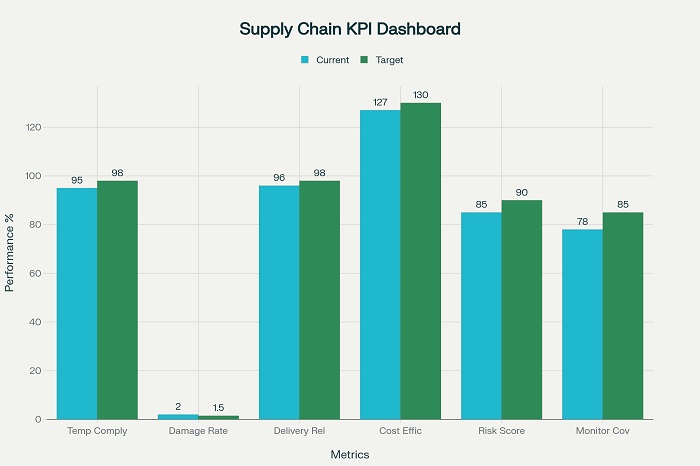
Total cost of ownership analysis evaluates all costs associated with pharmaceutical distribution packaging including material costs, transportation expenses, handling costs, and potential product losses due to packaging failures. This comprehensive analysis guides packaging selection decisions that optimize total costs rather than focusing solely on initial material costs. Total cost approaches often demonstrate that higher-quality packaging systems provide superior value through reduced product losses and operational efficiencies.
Transportation cost optimization through packaging design encompasses weight reduction, dimension optimization, and consolidation strategies that reduce shipping expenses while maintaining protection performance. Lightweight packaging materials and optimized dimensions enable more efficient transportation utilization while reducing fuel consumption and environmental impact. Packaging optimization can achieve transportation cost reductions of 20 to 35 percent while maintaining protection performance.
Operational efficiency improvements through packaging design optimization include easier handling, improved storage density, and reduced labor requirements that collectively reduce distribution costs while enhancing operational performance. Ergonomic packaging designs reduce worker fatigue and injury risk while improving handling efficiency. Stackable packaging configurations optimize warehouse storage density while facilitating automated handling systems.
The optimization of pharma packaging for shipping and distribution resilience represents a critical strategic capability that enables pharmaceutical companies to maintain reliable product delivery while managing costs and environmental impact. Through continued innovation in materials science, monitoring technologies, and design optimization, pharmaceutical distribution packaging will continue to evolve toward more sophisticated solutions that balance protection, efficiency, and sustainability while ensuring that essential medications reach patients safely and reliably. This evolution reflects the pharmaceutical industry’s commitment to supply chain excellence while demonstrating the critical role that packaging plays in global healthcare delivery and patient safety.