Traceability from Drug to Patient: Packaging as a Compliance Tool
The Critical Role of Pharmaceutical Packaging in Patient Safety and Supply Chain Security
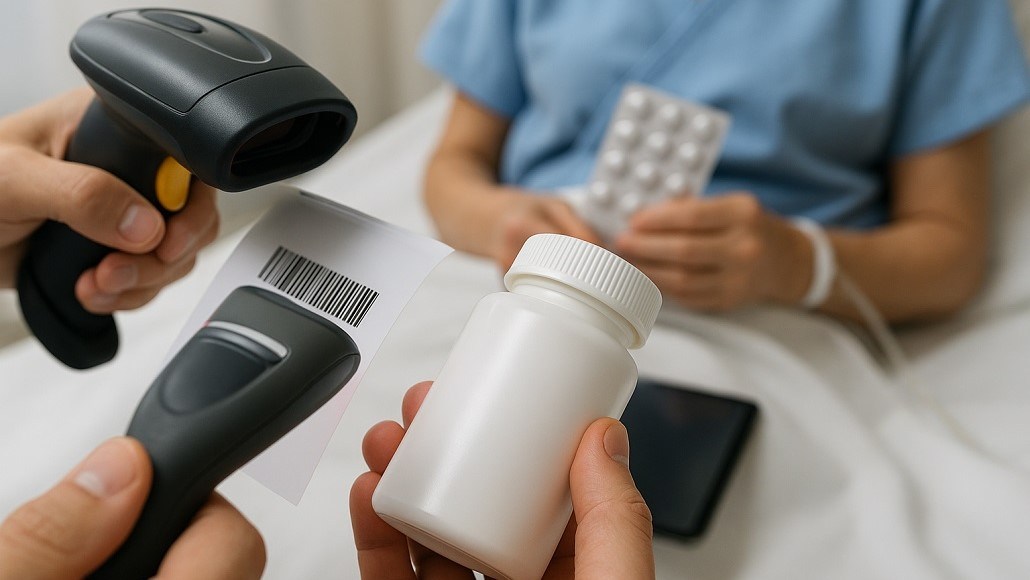
Pharmaceutical packaging traceability has emerged as a fundamental pillar of patient safety, supply chain security, and regulatory compliance in the modern healthcare ecosystem. The implementation of comprehensive traceability systems that follow medications from manufacturing through patient administration represents one of the most significant advances in pharmaceutical safety and quality assurance. These systems transform packaging from a simple protective barrier into an intelligent compliance tool that enables real-time monitoring, authentication, and tracking throughout the entire pharmaceutical supply chain.
The pharmaceutical industry’s commitment to traceability reflects growing recognition that patient safety extends far beyond the formulation and manufacturing of medications to encompass every step of the supply chain journey. Contemporary traceability systems utilize advanced serialization technologies, digital authentication methods, and blockchain integration to create comprehensive audit trails that protect against counterfeiting, enable rapid recall execution, and support regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions.
Recent implementation of the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) in the United States exemplifies the regulatory evolution toward comprehensive pharmaceutical traceability requirements. This legislation mandates electronic, interoperable systems that identify and trace prescription drugs throughout the distribution network, creating unprecedented levels of transparency and accountability in pharmaceutical supply chains. Similar regulations worldwide reflect the global commitment to pharmaceutical traceability as an essential component of public health protection.
Serialization Technologies and Implementation Frameworks
Pharmaceutical serialization represents the foundation of modern traceability systems, assigning unique identifiers to individual packages that enable tracking throughout the supply chain while supporting authentication and verification activities. These serialization systems utilize sophisticated data generation, printing, and verification technologies that ensure each pharmaceutical package receives a unique, tamper-evident identifier that supports comprehensive tracking and authentication.
The Global Standards One (GS1) framework provides standardized approaches to pharmaceutical serialization that ensure interoperability across manufacturers, distributors, and healthcare providers worldwide. This framework encompasses Global Trade Item Numbers (GTIN), serial numbers, lot information, and expiration dates that collectively create unique product identifiers. The standardized approach facilitates seamless data exchange across supply chain partners while supporting regulatory compliance in multiple jurisdictions.
Two-dimensional (2D) barcode technology has become the preferred method for encoding serialization information on pharmaceutical packages due to its high data density, error correction capabilities, and compatibility with various printing and scanning technologies. These barcodes encode comprehensive product information including manufacturer details, product identification, serial numbers, batch information, and expiration dates in machine-readable formats that support automated verification and tracking processes.
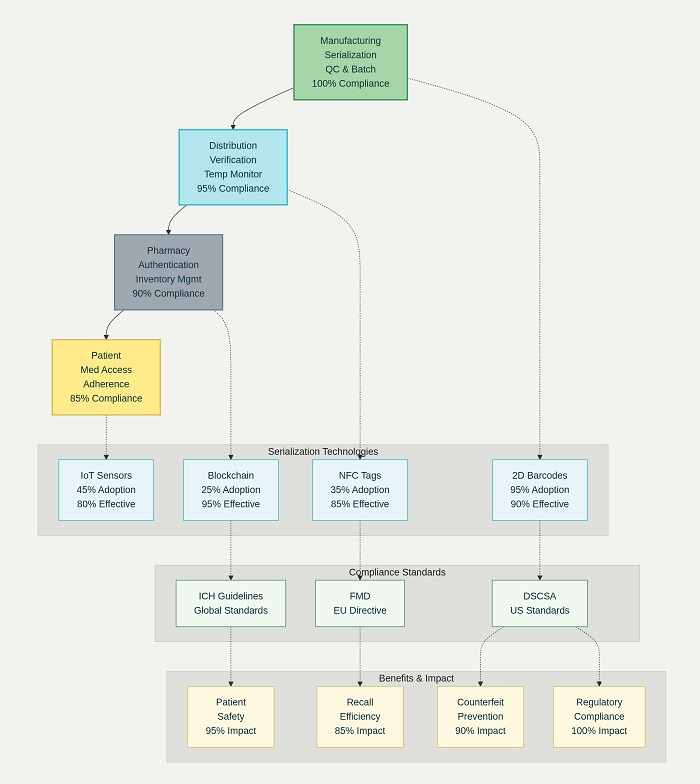
Aggregation technologies extend serialization capabilities by creating hierarchical relationships between individual units, cases, and pallets that enable tracking at multiple packaging levels. These systems create parent-child relationships that maintain traceability while supporting efficient handling and distribution processes. Aggregation enables comprehensive tracking of pharmaceutical products from individual units through bulk distribution while maintaining detailed audit trails required for regulatory compliance.
Authentication and Anti-Counterfeiting Measures
Advanced authentication technologies integrated with packaging traceability systems provide robust protection against pharmaceutical counterfeiting while enabling verification of product authenticity throughout the supply chain. These systems utilize multiple layers of security features that create comprehensive protection against sophisticated counterfeiting attempts while maintaining user-friendly verification processes for legitimate stakeholders.
Cryptographic authentication systems utilize advanced encryption algorithms to create tamper-evident digital signatures that verify product authenticity and supply chain integrity. These systems generate unique cryptographic codes for each pharmaceutical package that can be verified using secure authentication protocols. The cryptographic approach provides high-security protection against counterfeiting while enabling rapid verification using mobile devices and scanning equipment.
Blockchain technology has emerged as a powerful tool for pharmaceutical authentication by creating immutable records of product manufacturing, distribution, and handling activities. These distributed ledger systems provide transparent, tamper-proof documentation of pharmaceutical supply chain activities while enabling real-time verification of product authenticity and supply chain compliance. Blockchain implementation creates comprehensive audit trails that support regulatory compliance and investigation activities.
Physical authentication features integrated with serialization technologies provide additional layers of counterfeiting protection that complement digital authentication systems. These features include holographic elements, color-changing inks, and microprinting that provide visible authentication indicators while maintaining compatibility with automated verification systems. The combination of physical and digital authentication creates comprehensive protection against counterfeiting attempts.
Digital Health Integration and Patient Engagement
The integration of pharmaceutical traceability systems with digital health platforms has created opportunities for enhanced patient engagement, medication adherence monitoring, and adverse event reporting that extend the benefits of traceability directly to healthcare providers and patients. These integrated systems utilize mobile applications, Near Field Communication (NFC) technology, and QR codes to provide patients with access to comprehensive medication information while supporting adherence and safety monitoring.
Smart packaging technologies that incorporate NFC tags and QR codes enable patients to access detailed medication information, dosing instructions, and safety warnings using smartphone applications. These systems provide real-time access to updated product information while supporting medication adherence through reminder systems and usage tracking. The patient engagement capabilities create additional value from traceability investments while supporting improved health outcomes.
Electronic medication management systems integrated with packaging traceability enable healthcare providers to verify medication authenticity at the point of administration while maintaining detailed records of medication usage. These systems support medication reconciliation, adverse event reporting, and quality assurance activities that enhance patient safety while improving clinical workflow efficiency.
Pharmacovigilance integration with traceability systems enables rapid identification and investigation of adverse drug reactions while supporting targeted recall execution when safety issues are identified. These systems create direct links between patient experiences and specific pharmaceutical batches, enabling rapid investigation of safety concerns and implementation of protective measures.
Regulatory Compliance and International Harmonization
Pharmaceutical traceability systems must address comprehensive regulatory requirements that vary across jurisdictions while maintaining interoperability and data integrity throughout global supply chains. These requirements encompass data accuracy, system validation, audit trail completeness, and security measures that ensure traceability systems meet regulatory standards while supporting operational efficiency.
The European Union’s Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD) represents one of the most comprehensive pharmaceutical traceability regulations, requiring verification of prescription medications at the point of dispensing while maintaining comprehensive audit trails throughout the supply chain. This regulation has driven significant innovation in authentication technologies and verification systems while establishing standards that influence global traceability implementations.
FDA regulations under the DSCSA require comprehensive electronic tracking of prescription drugs throughout the distribution network, with full implementation creating an interoperable electronic system by 2024. These requirements encompass transaction information, transaction history, and transaction statements that create comprehensive audit trails while supporting verification and investigation activities.
International harmonization efforts facilitate global pharmaceutical traceability by establishing common standards and protocols that enable interoperability across regulatory jurisdictions. Organizations such as the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) work to develop unified approaches to pharmaceutical traceability that reduce compliance burden while maintaining rigorous safety and security standards.
Supply Chain Visibility and Risk Management
Comprehensive pharmaceutical traceability systems provide unprecedented visibility into supply chain operations that enable proactive risk management, quality assurance, and operational optimization. These systems create real-time monitoring capabilities that identify potential issues before they impact patient safety while supporting continuous improvement initiatives that enhance supply chain performance.
End-to-end visibility capabilities enable pharmaceutical companies to monitor product movement throughout global distribution networks while identifying potential disruptions, quality issues, or security concerns that could affect product integrity. This visibility supports proactive risk management strategies that prevent problems rather than responding to issues after they occur.
Temperature monitoring integration with traceability systems ensures that temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical products maintain required storage conditions throughout the supply chain. These systems provide real-time alerts when temperature excursions occur while maintaining detailed records that support quality investigations and regulatory compliance. The integration creates comprehensive cold chain monitoring that protects product integrity while providing documentation required for regulatory compliance.
Recall management capabilities integrated with traceability systems enable rapid identification and removal of affected products when safety issues are identified. These systems can quickly identify the location and distribution of specific batches while providing communication tools that facilitate rapid recall execution. The precision enabled by traceability systems minimizes the scope of recalls while ensuring complete removal of affected products.
Economic Benefits and Business Value Creation
The implementation of comprehensive pharmaceutical traceability systems provides substantial economic benefits that extend beyond regulatory compliance to encompass operational efficiency, risk mitigation, and business value creation. These benefits justify the investment required for traceability system implementation while providing ongoing returns through improved operations and reduced risks.
Brand protection benefits from traceability systems include reduced counterfeiting risks, enhanced consumer confidence, and improved market reputation that collectively support premium pricing and market share protection. Companies with robust traceability systems report improved customer loyalty and enhanced brand value that translate to measurable financial benefits.
Operational efficiency improvements through traceability system implementation include reduced recall costs, improved inventory management, and enhanced supply chain visibility that collectively reduce operating expenses while improving customer service levels. These efficiency gains typically achieve return on investment within three to five years while providing ongoing benefits throughout the system lifecycle.
Risk mitigation benefits encompass reduced liability exposure, improved regulatory compliance, and enhanced quality assurance that collectively reduce business risks while supporting long-term sustainability. The comprehensive documentation and monitoring capabilities provided by traceability systems support legal defense activities while demonstrating due diligence in pharmaceutical safety management.
Technology Innovation and Future Developments
The future of pharmaceutical traceability promises continued innovation in artificial intelligence integration, advanced analytics capabilities, and blockchain technology that will enhance security, efficiency, and functionality. These technological advances will create new opportunities for improving patient safety while reducing compliance costs and operational complexity.
Artificial intelligence applications in pharmaceutical traceability enable predictive analytics that identify potential supply chain disruptions, quality issues, and security threats before they impact operations. Machine learning algorithms analyze traceability data to identify patterns and anomalies that indicate potential problems while recommending preventive actions that maintain supply chain integrity.
Internet of Things (IoT) integration with traceability systems enables real-time monitoring of environmental conditions, handling activities, and storage parameters that affect pharmaceutical product quality. These sensor networks provide comprehensive data collection throughout the supply chain while supporting automated quality assurance and regulatory compliance activities.
Advanced analytics capabilities enable comprehensive analysis of traceability data to identify optimization opportunities, predict maintenance requirements, and enhance overall supply chain performance. These analytics platforms process vast amounts of traceability data to provide actionable insights that improve operations while supporting continuous improvement initiatives.
Patient Safety and Healthcare Outcomes
The ultimate value of pharmaceutical traceability lies in its contribution to patient safety and improved healthcare outcomes through enhanced medication authenticity, quality assurance, and adverse event monitoring. These safety benefits represent the most important justification for traceability system implementation while providing measurable improvements in public health protection.
Medication error reduction through traceability systems occurs through improved identification capabilities, enhanced verification processes, and comprehensive documentation that supports safe medication administration. Healthcare providers report significant reductions in medication errors when utilizing traceability-enabled verification systems that confirm medication authenticity and appropriateness.
Adverse event investigation capabilities enabled by traceability systems support rapid identification of causal factors and implementation of protective measures that prevent additional patient exposure. The detailed batch genealogy and distribution records provided by traceability systems enable precise investigation of safety issues while supporting targeted interventions that protect public health.
Quality assurance benefits from traceability systems encompass enhanced monitoring of manufacturing processes, distribution conditions, and storage parameters that affect medication quality and efficacy. These systems provide comprehensive documentation of quality-related activities while supporting continuous improvement initiatives that enhance pharmaceutical quality and safety.
The transformation of pharmaceutical packaging into a comprehensive compliance tool through traceability implementation represents one of the most significant advances in pharmaceutical safety and quality assurance. Through continued innovation in serialization technologies, authentication systems, and digital integration, pharmaceutical traceability systems will continue to evolve toward more sophisticated capabilities that enhance patient safety while supporting operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. This evolution reflects the pharmaceutical industry’s commitment to patient safety and quality assurance while demonstrating the potential for technology to create meaningful improvements in healthcare delivery and public health protection.